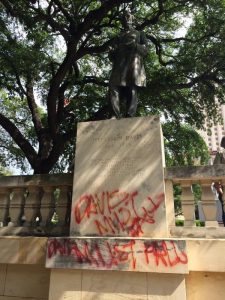By Jacqueline Jones and Henry Wiencek
In the late nineteenth century, white Southerners imposed a system of constraints on African Americans, denying blacks their Constitutional rights, and, indeed, their human rights. This system—often violently enforced—was called “Jim Crow,” named after a minstrel song that stereotyped blacks. It included the disfranchisement of black men, the forcible segregation of blacks from whites in public spaces, and forms of state-sanctioned terrorism such as lynching, which included hanging, mutilating, and burning victims alive.
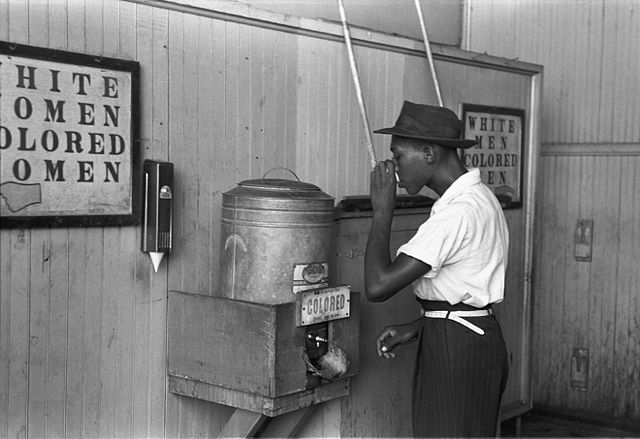

An African-American man drinking at a “colored” drinking fountain in a streetcar terminal in Oklahoma City, 1939. Courtesy of the Library of Congress.
“Jim Crow” shaped the South’s judicial and public education systems, employment structure, and patterns of landownership. Black people were limited to the most menial kinds of jobs, and sharecroppers found it difficult if not impossible to escape chronic indebtedness to their landlord-employers. In effect, white Southerners were determined to replace the institution of slavery with a new set of constraints enforced by white judicial officials, politicians, religious leaders, and lynch mobs.
For their part, African American Southerners protested “Jim Crow” by forming advocacy organizations, educational and religious institutions; boycotting and protesting against segregated facilities; and moving north.
The “Jim Crow” project included the creation of a white identity based in part on the glorification of the “Lost Cause”— the myth that before the Civil War, the south was an idyllic place populated by gracious planters and contented slaves. The Lost Cause found tangible expression in the many statues and other memorials dedicated to the Confederacy and the soldiers who fought for it.

Ku Klux Klan members and a burning cross, Denver, Colorado, 1921.The KKK was founded by former Confederate soldiers after the Civil War. Courtesy of the Library of Congress.
The erasure of slavery and “Jim Crow” from the historical record has distorted the teaching of U. S. history in both the South and the rest of the country. As communities finally begin to discuss and remove remnants of the Confederacy from public spaces, it is vital that all of us confront and fully understand this history.
Books:
James Allen, Without Sanctuary: Lynching Photography in America. Sante Fe: Twin Palms Publishers, 2000
Douglas A.Blackmon, Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II. New York: Anchor Books, 2008
David Cunningham, Klansville, U.S.A.: The Rise and Fallof the Civil Rights-Era Ku Klux Klan. New York: Oxford University Press, 2014.
Philip Dray, At the Hands of Persons Unknown: The Lynching of Black America. New York: Random House, 2002
Scott Ellsworth, Death in a Promised Land: The Tulsa Race Riot of 1921. Baton Rouge and London: Louisiana State University Press, 1982
David F. Godshalk, Veiled Visions: The 1906 Atlanta Race Riot and the Reshaping of American Race Relations. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2005
Gaines M. Foster, Ghosts of the Confederacy: Defeat, the Lost Cause, and the Emergence of the New South, 1865-1913. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988
Glenda Elizabeth Gilmore, Gender & Jim Crow: Women and the Politics of White Supremacy in North Carolina, 1896-1920. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1996
Grace Elizabeth Hale, Making Whiteness: The Culture of Segregation in the South, 1890-1940. New York: Pantheon Books, 1998
Louis R. Harlan, Booker T. Washington: the Making of a Black Leader, 1856–1901. New York: Oxford University Press, 1972
Louis R. Harlan, Booker T. Washington: the Wizard of Tuskegee, 1901–1915, Volume 2. New York: Oxford University Press, 1983
F. Michael Higginbotham, Ghosts of Jim Crow: Ending Racism in Post-Racial America. New York: NYU Press, 2013
Albert Kirwan, Revolt of the Rednecks: Mississippi Politics, 1876-1925. Lexington: University of Kentucky Press, 1951
J. Morgan Kousser, The Shaping of Southern Politics: Suffrage Restriction and the Establishment of the One Party South: 1880-1910. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1974
Kevin M. Kruse, White Flight: Atlanta and the Making of Modern Conservatism. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2005
J. Anthony Lukas, Common Ground: A Turbulent Decade in the Lives of Three American Families. New York: Alfred Knopf, 1985
Neil McMillen, Dark Journey: Black Mississippians in the Age of Jim Crow. Urbana, Ill: Illinois University Press, 1989
Michael Perman, Struggle for Mastery, Disfranchisement in the South. Chapel Hill and London: The University of North Carolina Press, 2001
Remembering Jim Crow: African Americans Tell About Life in the Segregated South, edited by William H. Chafe, Raymond Gavins, Robert Korstad. New York: The New Press, 2014
Slavery and Public History: The Tough Stuff of American Memory. Edited by James Oliver Horton, Lois E. Horton. New York: The New Press, 2006
LeRae Sikes Umfleet , A Day of Blood: The 1898 Wilmington Race Riot. Raleigh: Historical Publications Section, Office of State Archives and History, 2009
Articles:
Carl R. Weinberg, “The Strange Career of Confederate History Month,” OAH Magazine of History, Vol. 25, No. 2, Civil War at 150: Origins (April 2011), pp. 63-64
Elsa Barkley Brown and Gregg D. Kimball, “Mapping the Terrain of Black Richmond,” Journal of Urban History, 21, 3 (March 1995), 295-346
Fred Arthur Bailey, “Free Speech and the Lost Cause in the Old Dominion,” The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. 103, No. 2, “Play the Bitter Loser’s Game”: Reconstruction and the Lost Cause in the Old Dominion (Apr., 1995), pp. 237-266
Grace Elizabeth Hale, “Granite Stopped Time: The Stone Mountain Memorial and the Representation of White Southern Identity,” The Georgia Historical Quarterly, Vol. 82, No. 1 (SPRING 1998), pp. 22-44
Michael Martinez, “The Georgia Confederate Flag Dispute,” The Georgia Historical Quarterly, Vol. 92, No. 2 (Summer 2008), pp. 200-228
Jacquelyn Dowd Hall, “The Long Civil Rights Movement and the Political Uses of the Past,” Journal of American History 91, no. 4 (March 2005): 1233–63.
Kenneth O’Reilly, “The Jim Crow Policies of Woodrow Wilson,” The Journal of Blacks in Higher Education, No. 17 (Autumn, 1997), pp. 117-121
Reiko Hillyer, “Relics of Reconciliation: The Confederate Museum and Civil War Memory in the New South,” The Public Historian, Vol. 33, No. 4 (November 2011), pp. 35-62
Stephen A. Berrey, “Resistance Begins at Home:The Black Family and Lessons in Survival and Subversion in Jim Crow Mississippi,” Black Women, Gender + Families, Vol. 3, No. 1 (SPRING 2009), pp. 65-90
Documents:
Oral histories, videos and documents that specifically recount the Civil Rights Movement in Virginia
A two-volume Congressional report on Mississippi’s 1875 constitutional convention. Here is volume 1 and here is volume 2.
National Humanities Center, The Making of African American Identity
The Rise and Fall of Jim Crow, the website of this PBS special has stories, maps, documents, and activities for teachers.
You might also like these NEP articles on Slavery and its legacy in the US and further reading on Confederate flags, monuments, and historical myths.