by Adam Clulow with Ashley Gelato, Michael Rader, Izellah Wang and Alex Aragon.
In early 2020, we set about recruiting students for an experiment: Could four History majors design a fully functional, historically accurate video game across the course of a single semester. The experiment was driven, first, by an awareness of the dramatic growth of the video games industry in recent years and, second, by a sense that History departments including our own needed to engage more closely with what has become a key conduit for students in our classes.
At current estimates, video games are a $120 billion industry and one that is growing rapidly every year. For university students in particular, video games are pervasive. According to surveys, more than 70% of college students play video games, even more watch gaming content streamed on a range of services and the overwhelming majority report some exposure to video games across multiple platforms. At the same time, video games have become an increasingly important gateway for majors. Many students who enter our classrooms come to History via historically-based games which proliferate across multiple platforms.
Historians can engage with video games in two basic ways. First, we can deploy them much as a film or a novel to interrogate popular understandings of particular topics, moments or figures. Second, we can use them as a learning tool by asking students to design their own games. This was our approach. After an open call for applications followed by interviews, Julie Hardwick and I recruited four students, Ashley Gelato, Michael Rader, Izellah Wang and Alex Aragon, for a semester long Digital Humanities internship focused on game design, story-telling, programming, and history.
The task for the semester was to design a fully playable game that could be used in the classroom. The game was constrained by a set of guidelines. First, it had to be built around a historical episode known variously as Chushingura, the 47 ronin or the Akō incident. One of the most celebrated but also controversial episodes in Japanese history, the Akō incident took place between 1701 and 1703 and centered on an act of revenge carried out by a group of samurai against the perceived enemy of their dead master. It laid bare the tensions between the myths and the realities of samurai life in this period, between legality and morality, and between the need for order and the desire for honor.
Second, the Games Team had to develop a game with a clear educational payoff that could provide a window into the difficult life of a low-ranking samurai family in the eighteenth century. To ensure stability, the Tokugawa regime that governed Japan worked to preserve and secure the samurai class while also stripping them of the right to use violence. Placed on fixed stipends, many samurai and their families fell deeply into debt. The game had to draw on and make connections to the most recent scholarship on the lived realities of the Tokugawa samurai, providing a series of teaching points that educators could use to design lesson plans around. Third, the game had to be developed on zero budget, using only free, publicly available platforms and software without purchasing game assets. With these requirements in place, the Games Team was given total freedom to design the characters, the narrative and the game as a whole. As part of the internship, they worked closely with Ian Diaz, a UT graduate and experienced Games Designer.
Promotional video for the Ako game
Video games take many forms. Working within the confines of a single semester timeframe, the decision was made to develop a Visual Novel, a popular genre that is also highly flexible. Visual novels, which can broadly be characterized as Choose-Your-Own style adventure games, are typically presented in the first person with the player making a series of choices that govern subsequent actions. They employ branching storylines that offer multiple paths through the narrative and for this reason players often replay them to experience the full range of different options.
In designing a functional game, the Games Team faced four overlapping challenges: creating a believable central character, developing a branching storyline with consequential choices, writing compelling dialogue and producing realistic and historically grounded artwork. The most successful games push the player to invest emotionally in their character and the choices they make. The first hurdle, therefore, was to create a believable character that could stand at the center of a first-person game. The Akō game allows the player to view Tokugawa Japan through the eyes of young samurai, Kanpei Hashimoto. As Hashimoto, the player progresses through the major events of the Akō incident. The game is divided into four chapters with each chapter designed to expose Hashimoto to new decisions and conflicts while exploring the realities of samurai life, the economic structures of early modern Japan, the role of women in society, the commercialization of religion, and the nature of samurai ideologies in an age of peace.
Second, the Games team worked to construct compelling narratives filled with choices that matter. In total, the Akō game has five possible outcomes depending on the individual decisions players make. These five outcomes represent unique branches of the story, but the player is also presented with numerous smaller decisions that open up additional pathways.
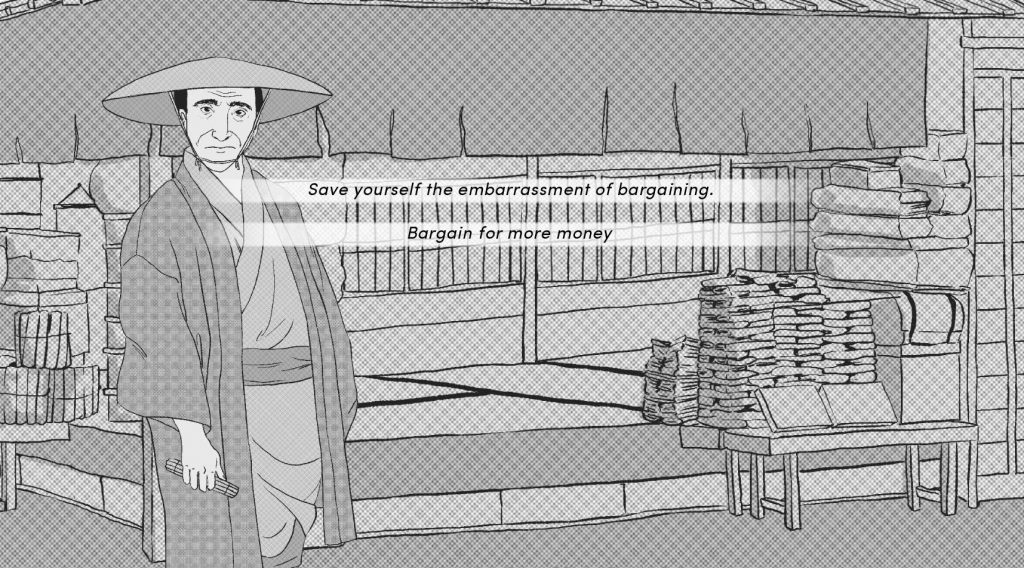
Third, the Games Team wrote thousands of words of dialog for use in the game. Visual Novels contain some background information that is displayed at key junctures in the story, but the vast majority of interactions take place through dialog as the player engages with individual characters. The scale of this dialog is magnified by the fact that it has to be written to accommodate multiple different pathways through the game. For this project, the Games Team wrote over 30,000 words of dialog, a significant challenge that required extensive research in topics as diverse as agriculture, diet, currency, dress style, architecture and funeral ceremonies.
Comments from Ashley Gelato, a member of the Games Design Team
Finally, the Games Team made the decision to develop original artwork rather than using public domain images. In its final form, the game has 4 chapters with 30 background images and 13 characters. Each of these 13 characters has multiple expressions, creating a total of around 50 individual “sprites” that display varying emotions and postures. In order to ensure that the artwork was historically grounded, hundreds woodblock prints and other images were collected to serve as reference material. Even the smallest of artistic decisions required extensive research.
Over the semester, the Games team dedicated hundreds of hours to the task. The result was impressive: a deep learning experience and a fully functional game, Ako: A Test of Loyalty, that is linked to contemporary scholarship. By the end of the semester in May 2020, the game was distributed to beta-testers who provided feedback. In September 2020, it will be used for the first time in a university setting as an educational resource and then released on commercial platforms where it will be available for download at no charge.

As an educator, it was remarkable to watch a group of students start from zero and build up an immersive historical experience over the course of a semester. Such experiments show how video games can be viewed as something more than just a distraction separated from the core study of history. Instead, used properly, video games can provide a highly effective vehicle for learning about the past. At UT, the experiment was so successful that it led directly to the creation of Epoch: History Games Initiative, which aims to develop a pipeline of historical games over the coming years.

You Might Also Like: