The year 2019 marks the 60th anniversary of the Tex-Son strike, a major labor battle waged in San Antonio, Texas from 1959 to 1963 by mostly Mexican, Mexican-American, and some Anglo women all of whom were active members of the International Ladies Garment Workers Union (ILGWU) Local 180. This strike is important for the history of Mexican Americans, women, and labor organization because it bridged the two other major moments for Mexican and Mexican American labor activism: the Pecan Shellers strike in San Antonio during the 1930s and the other Farah strike of the 1970s in El Paso. Little is known about labor activism strategies of marginalized women in the Southwest during the period in between these two infamous labor organizing efforts. The Tex-Son strike unveils what working women did to advocate for their needs on the garment factory floor during the Cold War period, especially in a historically anti-labor, anti-union state.

The Tex-Son strike was organized by the ILGWU, affiliated for most of its existence with the American Federation of Labor (AFL) and then the AFL-CIO when the AFL merged with the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) in 1955. By the mid-1930s, most of the garment industry moved to the Southwest as the region offered a low-cost labor pool of Black and Latinx workers. This industry transition proved to be complicated for the ILGWU as the union sent Anglo men with little experience in Spanish-speaking communities to represent workers in the Southwest. Eventually, the ILGWU maintained a presence in large cities in Texas, including San Antonio.
San Antonio was home to one of the largest populations of ethnically Mexican people in the United States, which the garment industry exploited for some of the lowest wages in the country. Many working-class ethnically Mexican women in San Antonio were able to obtain positions in the defense industry during WWII, but afterwards were left with slim options besides factory jobs. Tex-Son, owned by brothers Harold and Emanuel Franzel, employed both Anglo and Mexican American women, but were actively outsourcing work to Tupelo, Mississippi where Black women made up a lucrative labor force. In response to an uptick in union membership among Tex-Son workers by the ILGWU, the Franzels produced anti-union literature and warned their workers against signing any union agreements in the fall of 1958, before the strike began. In response, the ILGWU Negotiating Committee sent demands to the Franzels which included better wages and benefits among others.
The work of Gregoria Montalbo was essential to building momentum for the strike. An organizer from Chicago, her main job was to explain to hopeful recruits about the benefits and necessity of a strike against Tex-Son. Montalbo’s role as the president of Local 180 was focused on recruitment prior to the strike as well as working to gain support from San Antonio’s clergy during the strike, appealing to the many workers who were members of Catholic congregations in the city. One of the most committed clergy supporters was Father Sherrill Smith who agreed with Local 180 that San Antonio needed unions in order to create a more equitable work environment for everyone. He played a key role on the picket line and going door to door to recruit more people to join the strike.
The Tex-Son strike was the first to use an ILGWU Chicana lead organizer, Sophie Gonzalez, who became the face of the Tex-Son strike. Gonzalez began union organizing in 1949 after her brother, a union organizer for the Amalgamated Meatcutters and Butchers of America Union, encouraged her to accept a position in the ILGWU. Her presence in local newspapers and on the picket line was an integral piece of the ILGWU’s strategy. She maintained a certain physical appearance that portrayed her respectability as a woman but remained fierce in her communication of worker’s demands to the media and locals.
The very first week of the strike was the most tumultuous in terms of physical altercations between the women and allies on strike, the women who continued to work throughout the strike, and the police. On February 26th and 27th, the women on strike, angered by scab workers being escorted in and out of the factory, began throwing eggs and rocks at strike breakers and getting in physical altercations. The police charged the strikers with rioting and drunkenness, however there was not sufficient evidence to prove that any of the strikers were inebriated while on the picket lines.
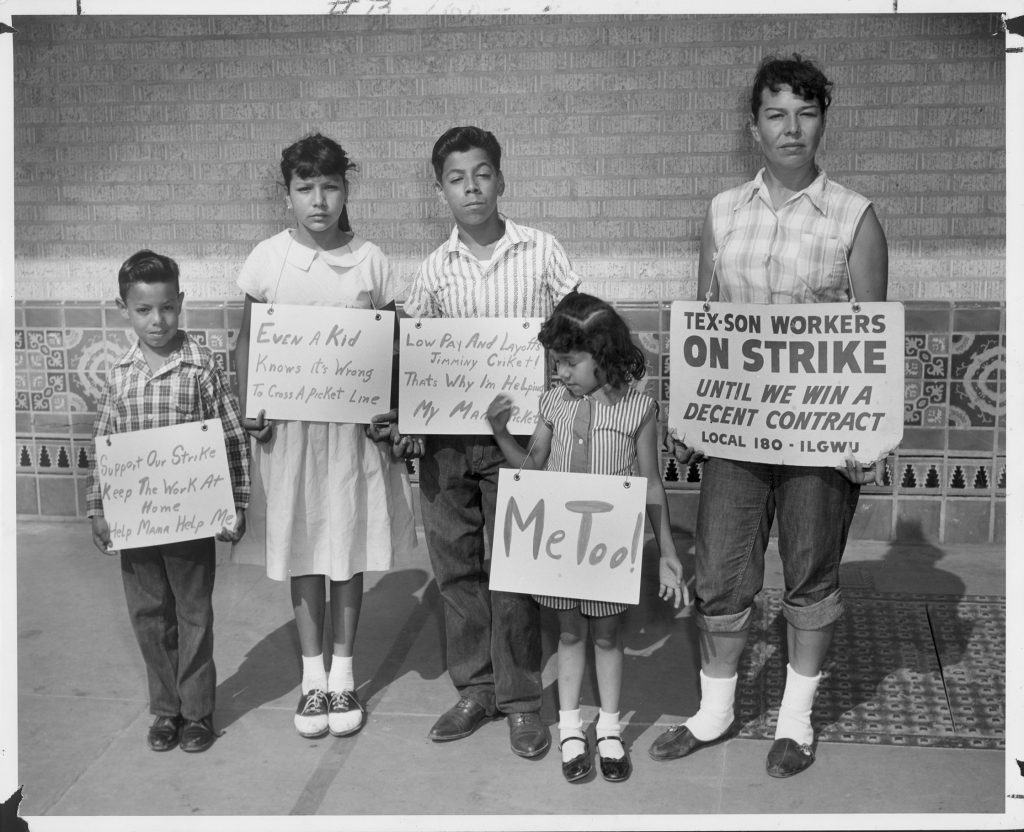

The ILGWU also engaged in a propaganda campaign to accompany the strike and boycott of Tex-Son goods. This campaign exploited the dominant ideology of the time about motherhood instead of on the women’s role as economic providers. In doing so, they produced materials such as reproducing checks given to Tex-Son employees next to pictures of their children, effectively communicating the inability to care for a family on such dismal paychecks. Even children participated by handing out balloons to other children entering surrounding department stores with “Don’t Buy Tex-Son Children’s Clothes,” imprinted on them. These tactics, however, were detrimental to the image of strikers as workers, not just mothers.
In the first year of the strike, the ILGWU women gained support from other local unions, such as the International Union of Brewery Workers, and other male supporters who assisted in picket line activities. However, the daily hardships that came along with picketing wore down many of the women who originally joined the strike. Many were forced to seek out other kinds of employment, especially after being blacklisted by Tex-Son, barring them from working at other garment factories. By September 1960, ILGWU strikers began to fear that their leadership was giving up on them, which eventually came to fruition when two months later, the small benefit checks from ILGWU stopped entirely and Gonzalez and other union leaders pulled out of the strike entirely. After appeals from people like County Commissioner Albert Peña Jr., the AFL-CIO office in Washington, D.C. agreed to continue to fund the remaining 80 women on the picket line. However, morale was already low and a few women complained that Gonzalez’s absence hurt the propaganda strategy. Others, however, complained that her leadership style and charges of opportunism hurt the strike from the very beginning. Ultimately, the strike lost its fervor due to continued violence perpetrated on the women and general distrust and lack of enthusiasm and financial support. By the end of 1962 the ILGWU pulled out of San Antonio altogether. On January 24, 1963, only eleven women were left on the last day at the picket line.
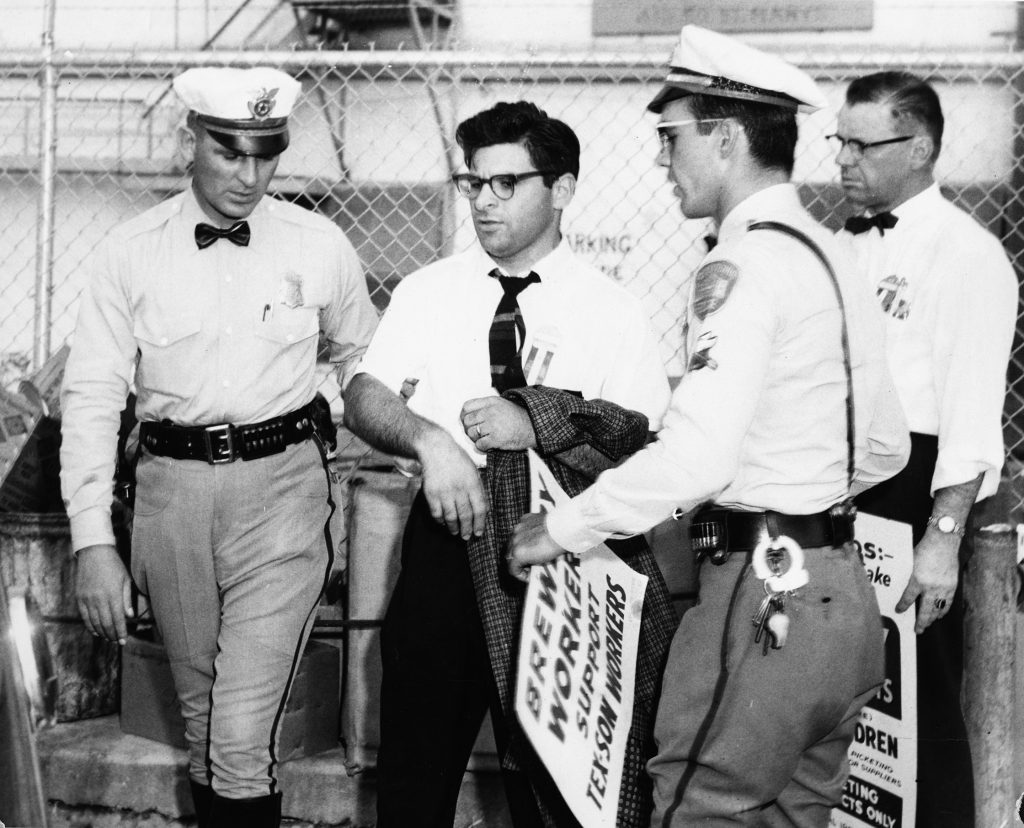

The consequences of an unsuccessful strike were clearly visible; after the ILGWU pulled out of San Antonio, unionism in the city remained practically absent. Many factories began to mock Tex-Son’s strategy of outsourcing work to the Deep South and across the U.S.-Mexico border. However, the Tex-Son strike is an important episode in the history of ethnically Mexican women’s Cold War era strategies to gaining labor rights for themselves. Blending public and private spheres by challenging the public to support their fight as mothers making ends meet for their families, the women presented locals with a new idea of women’s roles in the realm of labor. The Tex-Son strike also served as a primer of sorts for Texas Chicano Movement activism in the late 60s and early 70s that began to appeal to Chicanas’ racial and ethnic identity and oppression, rather than solely on gender identity and motherhood.
In addition to the historical importance, the strike also connects with current issues such as the recent Mississippi ICE raids at a poultry processing plant. Many observers suggest that the workers were targeted specifically because they successfully unionized and won a law suit against Koch Foods for $3.75 million over sexual harassment, national origin and race discrimination, and retaliation against Latinx workers. Although there are obvious differences between these two events, there are some salient congruencies. Both involved gendered discrimination and discrimination based on race and ethnicity. More obvious though, is the constant threats of violence that Latinx workers face then and today and their vulnerable position in exploitative labor relations. The Tex-Son strike and the unionization of the Mississippi poultry plant both ended in victory and defeat causing families to be uprooted and the loss of important sources of income. The immigrants detained by ICE are facing some of the most horrid conditions in detention and the women of the Tex-Son strike were beaten and chastised on the picket line. As different as the consequences of each are, the women involved share unsatisfactory and even dangerous work conditions alongside gender, ethnic, and national origin discrimination.
Sixty years after the beginning of the Tex-Son strike, Latinx people in the U.S. are still a major source of cheap labor and a punching bag for anti-union and anti-immigrant sentiments. Fortunately, strong labor activist roots for Latinx peoples of all nationalities and races still remain at the core of obtaining equitable working conditions. The Tex-Son strike of 1959, among others throughout the hemisphere, should be remembered as a foundation and lesson for labor activists today as anti-immigrant rhetoric is spewed from the highest bodies of government here and abroad.
This article draws on the following sources:
Lori Flores, “An Unladylike Strike Fashionably Clothed: Mexicana and Anglo Women Garment Workers Against Tex-Son, 1959-1963. Pacific Historical Review. 78, no. 3 (August 2009), 367-402.
Irene Ledesma, “Texas Newspapers and Chicana Workers’ Activism, 1919-1974. Western Historical Quarterly, 27, no. 3 (1995), 309-331
Vicki Ruiz, From Out of the Shadows: Mexican Women in Twentieth-Century America. 10th Anniversary Edition. New York: Oxford University Press, 2008.
More from Micaela Valadez:
City in a Garden: Environmental Transformations and Racial Justice in Twentieth-Century Austin, Texas by Andrew M. Busch (2017)
Dreaming with the Ancestors: Black Seminole Women in Texas and Mexico by Shirley Boteler Mock (2010)
Related Articles:
Goddess of Anarchy: Lucy Parsons, American Radical
Women Shaping Texas in the Twentieth Century
Textbooks, Texas, and Discontent: The Fight against Inadequate Educational Resources
The views and opinions expressed in this article or video are those of the individual author(s) or presenter(s) and do not necessarily reflect the policy or views of the editors at Not Even Past, the UT Department of History, the University of Texas at Austin, or the UT System Board of Regents. Not Even Past is an online public history magazine rather than a peer-reviewed academic journal. While we make efforts to ensure that factual information in articles was obtained from reliable sources, Not Even Past is not responsible for any errors or omissions.