In the study of history, it’s easy to fall back on national identities: “Irish music,” an “English accent,” “American Exceptionalism” are just a few examples. But a closer examination of the local cultures—music, dialects, history—that exist within nations demonstrates how misleading those generalizations can be. Just look through one of the British Library’s “Sound Maps” and you’ll be convinced. This remarkable site takes many of the library’s 50,000 recordings of music, regional accents, and oral histories and arranges them geographically on Google Maps. The project is at once global and local—each sound map is an aural window into a unique part of the world. You can hear birds chirping in Algarve, Portugal, a folksinger perform in Carlistrane, Ireland, or the local dialect in Morton, Mississippi.
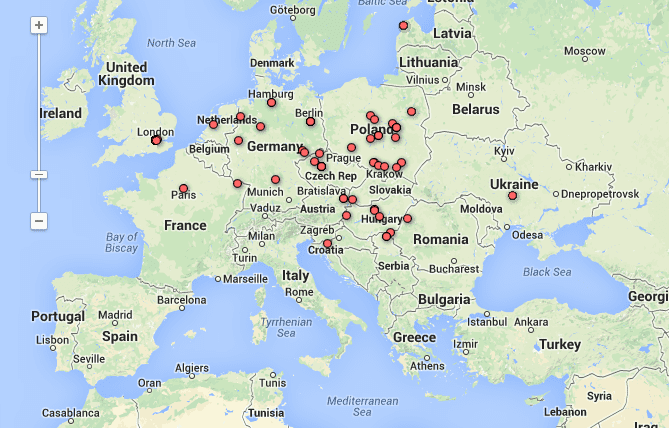
 One of the most fascinating—and addictive—features on the site is “Your Accents,” a global map of the world’s seemingly endless variety of dialects. The map features recordings of people from across the globe reading the same English phrases, allowing listeners to discern how each locality articulates “scone,” “garage” and “schedule” among other richly pronounceable words. The most immediate differences are apparent along national lines, as English, Indian, American, and various other accents contour the words in unique ways. But the map goes even deeper—revealing the astonishing regional differences that exist within those nations. Although people from Brighton and Leeds ostensibly share an “English” accent, the sonic differences between them are vast.
One of the most fascinating—and addictive—features on the site is “Your Accents,” a global map of the world’s seemingly endless variety of dialects. The map features recordings of people from across the globe reading the same English phrases, allowing listeners to discern how each locality articulates “scone,” “garage” and “schedule” among other richly pronounceable words. The most immediate differences are apparent along national lines, as English, Indian, American, and various other accents contour the words in unique ways. But the map goes even deeper—revealing the astonishing regional differences that exist within those nations. Although people from Brighton and Leeds ostensibly share an “English” accent, the sonic differences between them are vast.
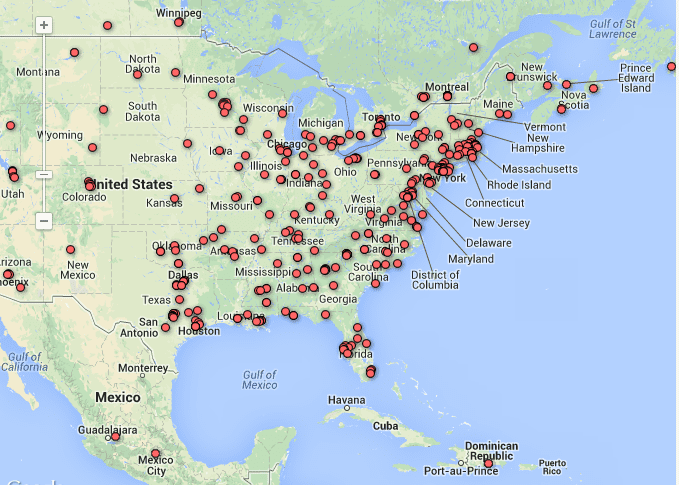
Other sound maps use the same technology to tell far more sobering stories. “Jewish Survivors of the Holocaust” archives oral histories of that traumatic epoch. Again using Google Maps, the page arranges survival stories based on geographic origins: individuals from France, England, Germany, Poland and even Azerbaijan are all represented. These unique and deeply affecting histories underscore the striking heterogeneity of the Holocaust’s victims and survivors. They were rich and poor; came from big cities and small towns; and identified as religiously devout and irreligious. By mapping their oral histories, the British Library visually captures that geographic and experiential diversity. And by letting them speak, reinforces the kinds of variations that get flattened out or even erased when reading text on a page.
 The British Library’s “Sound Maps” is an invaluable tool for anyone interested in hearing what the world sounds like. Cultural historians and preservationists will take particular interest in the collections of music and dialects—time capsules of old folkways quietly vanishing in a globalizing world. Readers may note the site’s emphasis on English speaking regions, especially the UK, but the geographic breadth of its collection remains deeply impressive. These maps do not just capture the sounds of the world, they capture its most compelling minutiae: the small town pubs, the remote jungles, and the fascinating people.
The British Library’s “Sound Maps” is an invaluable tool for anyone interested in hearing what the world sounds like. Cultural historians and preservationists will take particular interest in the collections of music and dialects—time capsules of old folkways quietly vanishing in a globalizing world. Readers may note the site’s emphasis on English speaking regions, especially the UK, but the geographic breadth of its collection remains deeply impressive. These maps do not just capture the sounds of the world, they capture its most compelling minutiae: the small town pubs, the remote jungles, and the fascinating people.
Explore the latest finds in the NEW ARCHIVE:
Charley Binkow on iTunes’s salute to Black History Month
And Henry Wiencek finds a new way of looking at Emancipation
Photo Credits:
Screenshot from “Your Accents” sound map (Image courtesy of the British Library)
Screenshot from “Jewish Survivors Of The Holocaust” sound map (Image courtesy of the British Library)
Quebecois lumbermen making music with a violin and sticks, 1943 (Image courtesy of National Film Board of Canada)