Cross-posted from Chris Rose’s blog, where he regularly tells us Important and Useful Things and makes us laugh along the way. In addition to his many other accomplishments, Chris is the brains and motor behind our podcast, 15 Minute History.
Over the weekend, the Thomas Cook company went bankrupt and shuttered operations, leaving hundreds of thousands of people stranded worldwide and searching for flights home.
A number of us Twitterstorians became particularly concerned about the impending demise of the company a few days ago when Ziad Morsy, a martime archaeologist and Ph.D. candidate at the University of Southampton tweeted that Thomas Cook’s historical archivist had lost his job.
https://twitter.com/ziad_morsy/status/1175998560178974720?s=20
The Thomas Cook company was 178 years old when it collapsed (just over a month before Britain may or may not exit the European Union–coincidences which have been commented upon elsewhere). Some of its history in relation to British imperial history was covered by another colleague in a Twitter thread yesterday:
Thomas Cook began leading tour groups to Egypt and the Holy Land 150 years ago in 1869. He was even present at the opening ceremoy of the Suez Canal in November that year. So began the history of modern Western organized tourism in the Middle East. pic.twitter.com/0pQjxNd60H
— Belated Antiquity (@afzaque) September 23, 2019
Inasmuch as it’s easy to point to the Thomas Cook Company’s early days as those of a commercial company essentially making money off of the expansion of the British Empire, there are occasional glimpses at a richer and more complicated role for the company in various contexts (@afzaque covers several of them in his thread, which is worth a read).
It’s these sorts of things that make the potential loss of the company’s archive particularly painful, as it is one of those out-of-the-box sources for material that can shed startling new light on historical periods.
And hence, I present …
The curious case of the Thomas Cook Hospital
I ran across the hospital while writing the first two chapters of my dissertation, which wound up comprising a comprehensive history of public health in Egypt between 1805 and 1914 as one did not already exist. (Wanna publish it? It’s not going to be in the monograph.)

The West Bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor, in 2010.
It was located in Luxor, a settlement that is notable mostly for what people were doing there thousands of years ago, as it is built on top of the ruins of what was almost certainly not known to its inhabitants as Thebes, but was one of the New Kingdom capitals of ancient Egypt. Across the Nile River, wide and lazily flowing at this point, is the pyramid-shaped hill that marks the location of the Valley of the Kings.
Given the numerous pharaonic sites that dot the landscape up and down the river from Luxor, Cook had the bright idea to utilize boat travel for wealthy tourists to visit them without the hassle of having to move constantly to new hotels every night. Luxor, at the epicenter, was the site of the train station from which Wagon-Lits and other operators operated sleeper trains to Cairo.
In 1890, Luxor was a small town — perhaps five thousand permanent inhabitants, which could swell as high as twenty thousand during tourist season when there was work to be had.
John Mason Cook–the son referred to in the company’s official name “Thomas Cook & Son” after 1865 — had the idea to open a hospital as early as 1887:
In 1887, he decided, driven by the reactions of rich foreigners–British, American, German–in the face of the unfortunate hygienic conditions of the local population, to construct a hospital. “Accomplished in 1891, inaugurated by the Khedive Tewfik Pacha, it comprised 26 beds (of which 8 were for women, 10 for men)*, the buildings well constructed, each isolated from the other, in a healthy and fortuitous position.”
*(no, this doesn’t equal 26).
Jagailloux, Serge. La Médicalisation de l’Égypte Au XIXe Siècle. Synthèse 25. Paris: Éditions Recherche sur les civilsations, 1986. (translation mine).
The hospital was co-directed by a Syrian doctor and an Englishman (only the latter–a Dr. Saimders–is named). Given that neither were in residence in Luxor in the off season (April to November), a third doctor–an Egyptian–was appointed to see patients in the off-season.
It was estimated that over 120,000 patients were seen, with over 2,000 operational procedures performed, in its first twenty years of operation. The hospital was presumably built primarily for the treatment of visiting foreigners, with Egyptians working in the tourist industry as a secondary priority.
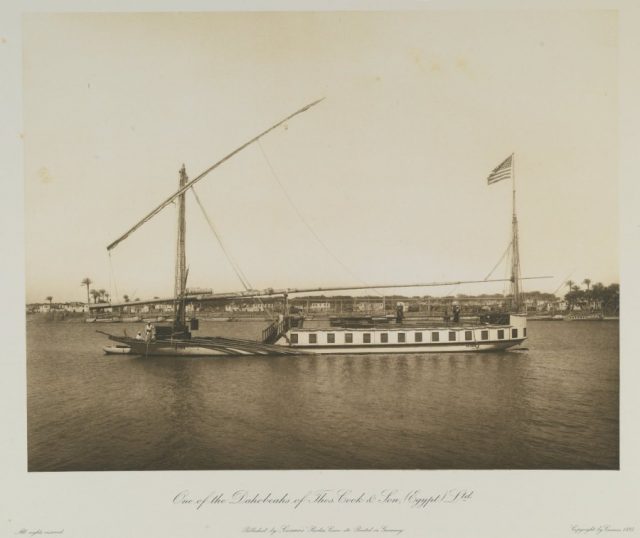

“One of the Dahabeahs (sic) of Thos. Cook & Son Company (Egypt)”
Berlin: Cosmos art publishing Co., 1893.
Collection of the Brooklyn Museum
What is interesting is that, with Cook’s blessing, the hospital was opened to the public as well. In 1898, The Lancet enthusiastically reported that people were coming from over two hundred miles away to seek treatment at the facility. (“Egypt.” The Lancet 152, no. 3905 (July 2, 1898): 59.)
After the British occupation in 1882, funding for public health flatlined. Under Lord Cromer, the public health budget never exceeded 100,000 Egyptian pounds (at the time LE 1 = £0.95).
Hospitals in the provinces, which were already run down and developing a bad reputation among patients (most of them had been built in the 1840s), were frequently closed or moved to other, newer buildings that were not purpose-built to serve as hospitals.
The construction of private facilities was encouraged by the Anglo-Egyptian government; the government would not open new hospitals or dispensaries (a combination pharmacy/clinic used to supplement hospitals in smaller settlements) in towns that had “good” private facilities. Many of the hospitals were funded by local European communities to serve their own–Austro-Hungarians, French, Greeks, Italians, and Anglo-Americans all had their own facilities in Cairo and/or Alexandria, most of which referred their Egyptian patients to government facilities.
Hence, it is a point of curiosity for me as to what inspired John Mason Cook to open his hospital to the general public, especially given that his company did not lack for wealthy clientele to fill its beds.
It suggests that, even at the height of imperialism, with a company that can (and has) be considered an agent of an imperial power, things are never quite as simple as they might seem.
As I was writing this, Ziad tweeted me this tantalizing entry from the archival catalog:
https://twitter.com/ziad_morsy/status/1176877234487009281?s=20
Hence, the answer to my questions may lie in this box, whose future is now in doubt.
What you can do to help
If you’re one of us history types who has benefitted, or could benefit, from consulting the Thomas Cook archives, this thread has specific action items you can take to let people know that there is interest in saving the archive and not letting its contents be dispersed or destroyed.
People: you've seen the bad news about Thomas Cook. We *urgently* need to secure the archives, hugely important in the history of transport & mobility.
— JTH Official (@JTransportHist) September 23, 2019
If you've used the archives, or have an interest, please help! Letters of support needed – pls contact Mike Anson: @BAC_Chair
More by Christopher Rose:
You’re Teaching What?
Wrong About Everything
Searching for Armenian Children in Turkey: Work Series on Migration, Exile, and Displacement
Exploring the Silk Route
You Might Also Like:
2019 History PhDs on Not Even Past
An Apology for Propaganda
Anxieties, Fear, and Panic in Colonial Settings: Empires on the Verge of a Nervous Breakdown edited by Harald Fischer-Tiné (2016)
The views and opinions expressed in this article or video are those of the individual author(s) or presenter(s) and do not necessarily reflect the policy or views of the editors at Not Even Past, the UT Department of History, the University of Texas at Austin, or the UT System Board of Regents. Not Even Past is an online public history magazine rather than a peer-reviewed academic journal. While we make efforts to ensure that factual information in articles was obtained from reliable sources, Not Even Past is not responsible for any errors or omissions.