The European Enlightenment occurred as an ongoing dialogue of ideas—a discourse composed of voices from around the globe. As Daniela Bleichmar demonstrates, southern Europe, long ignored in scholarship on the Enlightenment, had a crucial voice in the conversation.
In Visible Empires, Bleichmar claims that Imperial Spain, more than any other contemporary empire, used visual documents like paintings and maps to make the empire tangible and, in this way, “governable.” Images, she argues, made visible the hidden or secret. Bleichmar highlights the Hispanic World’s investment in knowledge production at the peripheries of empire. She emphasizes how scientific investigations, specifically botanist and natural history expeditions, fit into the Spanish Empire’s attempt to reestablish itself as a European political and economic power in the late eighteenth century. Her findings demonstrate how relationships between the center and periphery of empire were often a matter of perspective.
Bleichmar makes use of the long ignored and beautiful visual archive of botanical paintings produced by Spanish expeditions around the Atlantic. She reads these centuries-old detailed depictions of flora and fauna to stress the relevance of vision to governing of the empire. For Spain, these illustrations provided visual evidence of worlds across the sea and of our ability to understand nature. They buttressed Spain’s ownership of the unseen. The Spanish metropole also used this method to understand the racial compositions of distant populations. New Spain’s casta paintings and Peru’s taxonomical illustrations gave the metropole a window into their kingdoms abroad. Simultaneously, the project supplied the peripheries of empire with the agency to codify their populations. While knowledge of its far-off inhabitants gave the metropole a sense of discovery and ownership, the power to produce pictures of their world gave people on the periphery power of their own.
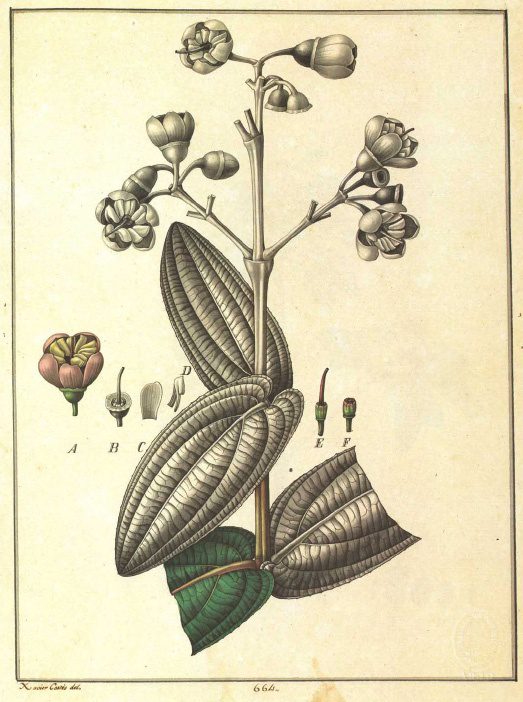
![An image from "Flora Huayaquilensis," a visual collection of South America's plants as seen by Spanish botanist Juan José Tafalla during a 1785 expedition through Peru and Chile. ([Juan Tafalla], “Flora Huayaquilensis,” ourheritage.ac.nz | OUR Heritage - See more at: http://otago.ourheritage.ac.nz/items/show/7696#sthash.r8R9WHhx.dpuf)](https://notevenpast.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/87bbce75b1706f7ba39ef9bcbb7c9560.jpg)
An image from “Flora Huayaquilensis,” a visual collection of South America’s plants seen by Spanish botanist Juan José Tafalla during a 1785 expedition through Peru and Chile. ([Juan Tafalla], “Flora Huayaquilensis,” ourheritage.ac.nz | OUR Heritage)
During the Enlightenment, intellectuals and others contested and refined the themes of art, science, and knowledge using visual representations. The “correct” representation did not always come from the center or metropole but, as Bleichmar explains, it was often difficult to tell where in the empire botanical Enlightenment projects began. Indeed, knowledge moved in multiple directions. Bleichmar explores how some naturalists understood colonial agendas in ways that differed from the intentions of the Spanish metropole. Consider Basco y Vargas’ pepper initiative in the Philippines. He prioritized his local economic goals over the philosophical inquiries coming from Spain. In this case, the periphery directed knowledge production as Basco y Vargas determined what botanical investigation to support.
Allegiances and relationships to a “center” thus differed depending on local context. However, by suggesting “the goal of this intensive natural history investigation… was nothing less than to rediscover and reconquer the empire at a time of intense crisis,” Bleichmar seems to suggest that Spain held more control over the direction of knowledge production. In addition, the author admits that the only a limited audience saw or studied the visual illustrations produced by enlightenment botanist. These minor inconsistencies leave the reader with a lingering question: to what extent did “visual” knowledge shape the empire at large?
Aside from images, Bleichmar also examines the tremendous written archive that preserves the voices of botanist and economists. While historians typically use images in their work without fully exploring the significance they held for their creators, the author’s examination of written sources provides the reader with a fuller understanding of the botanical illustrations. Paired with Bleichmar’s engaging prose, Visible Empires constitutes a thorough interpretation of southern European Enlightenment and provides a fine example of a historical investigation achieved with beautiful visual sources.
More books on Early Modern science:
Jorge Cañizares Esguerra’s review of Shores of Knowledge: New World Discoveries and the Scientific Imagination
Laurie Wood’s review of The Discovery of Jeanne Baret: A Story of Science, the High Seas, and the First Woman to Circumnavigate the Globe