In the spring of 1852, Benjamin Roper, overseer to Galveston area plantations Evergreen and Headquarters, wrote a short letter to his employer to inform him that “on the night of [April] 30 I cut Lewis [an enslaved man] with a knife . . . . He is now and has been since his misfortune at Dr. Whiting’s and will remain there until he is able to bear punishment when I shall bring him home and give him a very severe whiping [sic].” Roper postponed describing the events leading up to this act of brutality, however, he insisted that “if any negro (whether I have the controll [sic] of him or not) should ever give me the like provocation, I will deliberately take his life. I am now armed and it is my intention never to go into your field without, and to use them if necessary.”

The recipient of this missive was Ashbel Smith, noted Texas statesman often hailed as both “the father of Texas medicine” and “the father of the University of Texas.” Known for his pioneering work in the treatment of yellow fever as well as his diplomatic endeavors, Smith spent the latter part of his life acting as a vocal proponent for women’s and African American education, serving as one of three commissioners tasked with establishing an “Agricultural and Mechanical College of Texas, for the benefit of the Colored Youths”—the institution that would eventually become Prairie View A&M University. This avowed investment is difficult to reconcile, however, with Smith’s years-long, active participation in the institution of chattel slavery, including his seeming complicity in his steward’s violent attempts at plantation management.
Shortly after the April 30 incident, Smith returned to his Texas holdings for a brief visit, after which Roper penned a follow-up message noting, “Lewis is here for a week or two until we get more out of the grass. Perhaps it may be some satisfaction for you to know that he as well as all the other negroes have behaved very well indeed since you left.” This bit of self-congratulation would prove premature, however, as between the writing of this letter and one dated June 23, 1852, those enslaved by Ashbel Smith mounted a sustained resistance (undoubtedly, at least in part, to Lewis’ stabbing) that would compel Roper to draft yet another letter to his employer noting that “Your negroes have for a long time enjoyed the reputation of being hard to manage yet I believed until now that I could control them. I am now satisfied that I cannot and being so satisfied I wish to resign.” It is clear from this communication that, as they had done in years past, the individuals enslaved by Ashbel Smith were challenging the conditions of their enslavement. This is evident in Roper’s comment a week later that “whilst I have been at one place [that is, one of Smith’s plantations] the work has been neglected at the other. Your negroes all need continual watching or rather continual flogging to make them do their work.”
Demoralized, Roper divulges that “there is not a single person [enslaved at Evergreen or Headquarters] in whom I can depend unless it be Abram, and I have not full confidence in him. Bob and Old Sam deceived me for a long time but I have found them out and in my opinion there are not two greater scoundrels on the place.” Roper’s plaintive airing of grievances highlights how those enslaved by Smith shifted the balance of power after a heinous act of violence, contesting the circumstances under which they were expected to labor in ways marking them, in Roper’s view, as “scoundrels.”
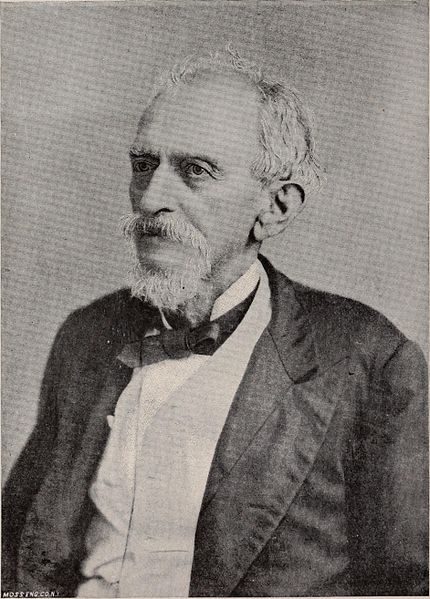

This situation was thrown into crisis once again in 1857, as Ashbel Smith began to receive extensive correspondence from Roper concerning the practices of his replacement, the newly hired overseer, Mr. Page. Roper still lived in the area and spoke regularly with Smith. In February 1857, he wrote to note that Page was rarely if ever seen in the fields and that, rather, “the negroes are called up and receive orders at the house and then they go off and do as they please.” While this lack of oversight may have been to the benefit of the enslaved on one hand, it signaled a type of neglect that would leave them especially vulnerable to medical calamity, on the other. On March 4, 1857, Roper writes, “Ann gave birth to a [daughter] since you left which died a few days after. I knew not of its birth or sickness until after its death, if I had I should have gone to have seen it.” He adds, “I have since told Albert and Abram that if anyone was sick hereafter before your return to let me know it”—a request that seems to imply that Roper attributes the death of Ann’s child to some failure to attend to the needs of those enslaved on Evergreen Plantation on Mr. Page’s part.
Such was the fate of these individuals: despite Smith’s reputation as an upstanding and altruistic Texas luminary, the people he enslaved spent their lives subject to the whims of a perpetually absent “master” and were routinely made to contend with insufficient resources, violent overseers, and inadequate health care.

Read the full letters from the Ashbel Smith Papers, 1823-1926 here:
- Letter from May 3, 1852
- Letter from June 1, 1852
- Letter from June 23, 1852
- Letter from June 30,1852
- Letter from Feb 2, 1857
- Letter from March 4, 1857
Sources:
Ashbel Smith Papers, 1823-1926, Dolph Briscoe Center for American History, The University of Texas at Austin.
“Evergreen Plantation.” Handbook of Texas Online.
Elizabeth Silverthrone. “Smith, Ashbel.” Handbook of Texas Online.
You might also like:
White Women and the Economy of Slavery
Love in the Time of Texas Slavery
Slavery World Wide: Collected Works from Not Even Past
The views and opinions expressed in this article or video are those of the individual author(s) or presenter(s) and do not necessarily reflect the policy or views of the editors at Not Even Past, the UT Department of History, the University of Texas at Austin, or the UT System Board of Regents. Not Even Past is an online public history magazine rather than a peer-reviewed academic journal. While we make efforts to ensure that factual information in articles was obtained from reliable sources, Not Even Past is not responsible for any errors or omissions.



