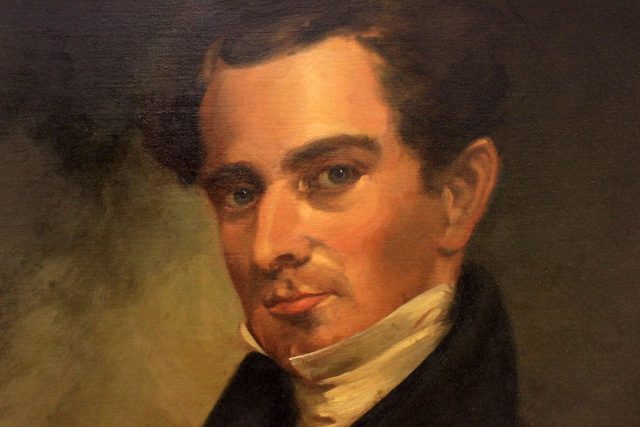UT Austin students know the name Castañeda as one-half of the namesake of the Perry-Castañeda Library. Perhaps fewer appreciate the profound impact that the eminent historian, librarian, and social reformer Carlos E. Castañeda exerted upon their University, the field of Texas history, and the Mexican American civil rights struggle in Texas. A two-day symposium to take place at UT Austin this fall offers a chance to reexamine the life, work, and scholarly and social impact of this pivotal figure.
2023 is an appropriate time to reassess Castañeda’s legacy. This year marks the centenary year of the founding of the Texas Historical Commission in 1923, a body sponsored by the Knights of Columbus that also published Castañeda’s seven-volume Our Catholic Heritage in Texas (1936-1958). This work stands as a veritable monument in Texas historiography.
In commemoration of this centenary, UT Austin’s Matthew Butler and History Department alumnus Brian Stauffer (PhD, 2015) have organized “Castañeda’s Catholic Texas?” to reappraise Castañeda’s historiographical legacy as Texas’s preeminent Mexican American historian. The event will also contextualize this intellectual work within his Catholic faith and a lifetime of labor and political activism.
Castañeda was,both, a Catholic and a papal knight whose commitment to human dignity and spiritual militancy led him to campaign against discrimination in Texas employment practices as a field officer in FDR’s Fair Employment Commission and in favor of Mexican Americans’ educational and civic rights as a school superintendent and member of LULAC (League of United Latin American Citizens). To this end, the organizers have assembled a diverse group of scholars whose work will collectively reevaluate Castañeda’s contribution to the lived history and historiography of twentieth-century Texas and his Catholic ideas, while taking Castañeda’s work as an inspiration for new Catholic and labor histories of Texas and the Border.
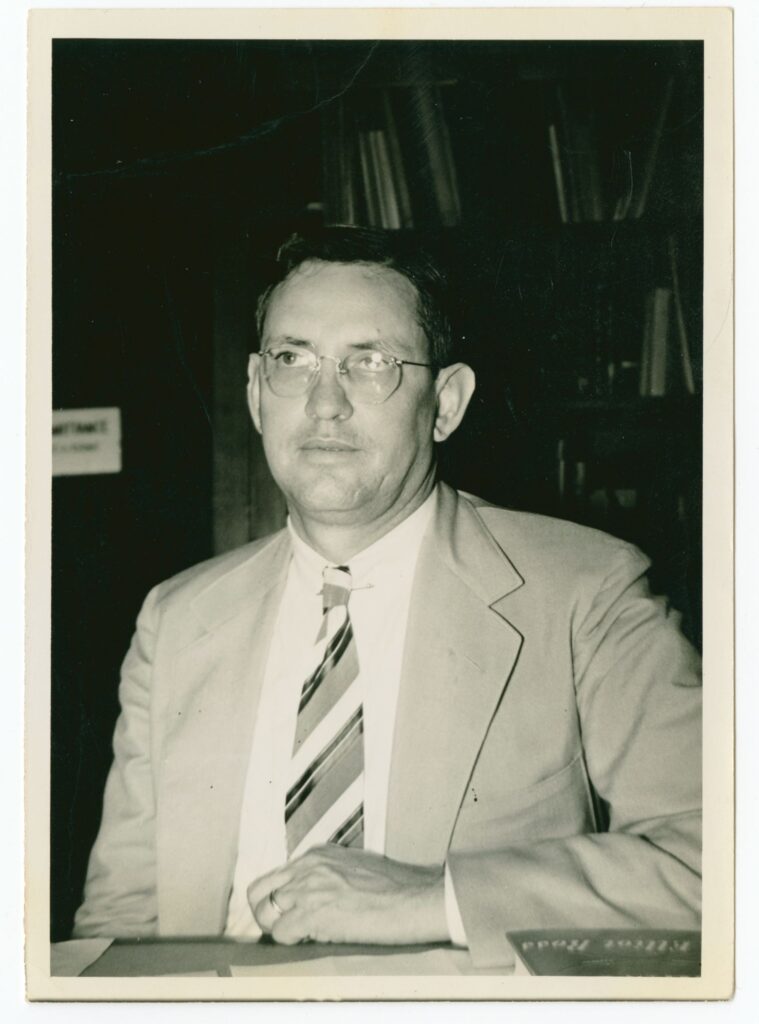

Despite his reputation as a confessional historian and Boltonian—an admirer of Herbert E. Bolton’s theory of the Borderland as an interactive imperial space[1]—Castañeda was a multifaceted, politically engaged, and paradoxical figure. Though his writing lauded the presence of Spanish missionaries in Texas and sometimes adopted their view of Indigenous people as backward and childlike, Castañeda himself faced discrimination at the hands of an ethnocratic power structure convinced of Mexican inferiority.
A Catholic who collaborated with exiled Mexican priests, such as Jesuit Mariano Cuevas, Castañeda nonetheless supported the Mexican Revolution’s educational project and was an interlocutor of the most anticlerical regime in hemispheric history. Best known as a historian-archivist (in correspondence he enjoyed describing himself as “the Historiographer”), Castañeda’s activism as Del Río school superintendent, on the U.S. Committee on Fair Employment Practice, or in pro-Hispanic organizations such as LULAC, perhaps outlasts his intellectual achievements.

Why is it that a historian of colonial, Catholic Texas should loom so large as a labor activist and defender of Mexican American rights in the twentieth century? In what overlooked, unheralded ways did Castañeda’s Catholicism and intellectual work lead him to espouse what were then radical political views and activist roles? “Castañeda’s Catholic Texas?” will explore these tensions between Castañeda’s historical imagination and activist life. It will also feature new contributions to the historiography of Catholicism in Texas that build upon Castañeda’s monumental work, taking it as a starting point for new, critical discussions of the interactions between faith, politics, and identity. Other contributions, such as that of UT Austin’s Emilio Zamora, will recontextualize Castañeda’s struggle on behalf of Mexican American workers.
Symposium participants will address three major themes in as many sessions: Castañeda’s intellectual work as a Catholic and Mexican historian in Texas; histories of Texas that carry his historiographical ideas forwards; and histories of Castañeda’s labor and political activism. Panelists include UT Austin faculty members Matthew Butler, John Moran González, and Emilio Zamora, along with Juliana Barr (Duke), Fr. Robert E. Wright, OMI (Oblate School of Theology), Deborah E. Kanter (Emeritus, Albion College), Gerald Poyo (St. Mary’s), Roberto R. Treviño (Emeritus, UT-Arlington), Jesús F. de la Teja (Emeritus, Texas State), Ricardo Álvarez-Pimentel (Baylor), Timothy Matovina (Notre Dame), Cynthia E. Orozco (Eastern New Mexico University), Matthew Gritter (Angelo State), Maggie Elmore (Sam Houston State), and Aaron E. Sánchez (Texas Tech). The symposium is sponsored by the Institute for Historical Studies in the History Department, the Texas Catholic Historical Society, the Nettie Lee Benson Latin American Collection, UT Libraries, and the Summerlee Foundation.
The symposium will be held in the Second Floor Conference Room of the Benson Collection’s on-campus home in Sid Richardson Hall (SRH.1) on September 20-21, 2023. Additional updates and registration details will be released in August. Further inquiries about the event can be directed to tchs@txcatholic.org.
[1] https://www.tshaonline.org/handbook/entries/bolton-herbert-eugene