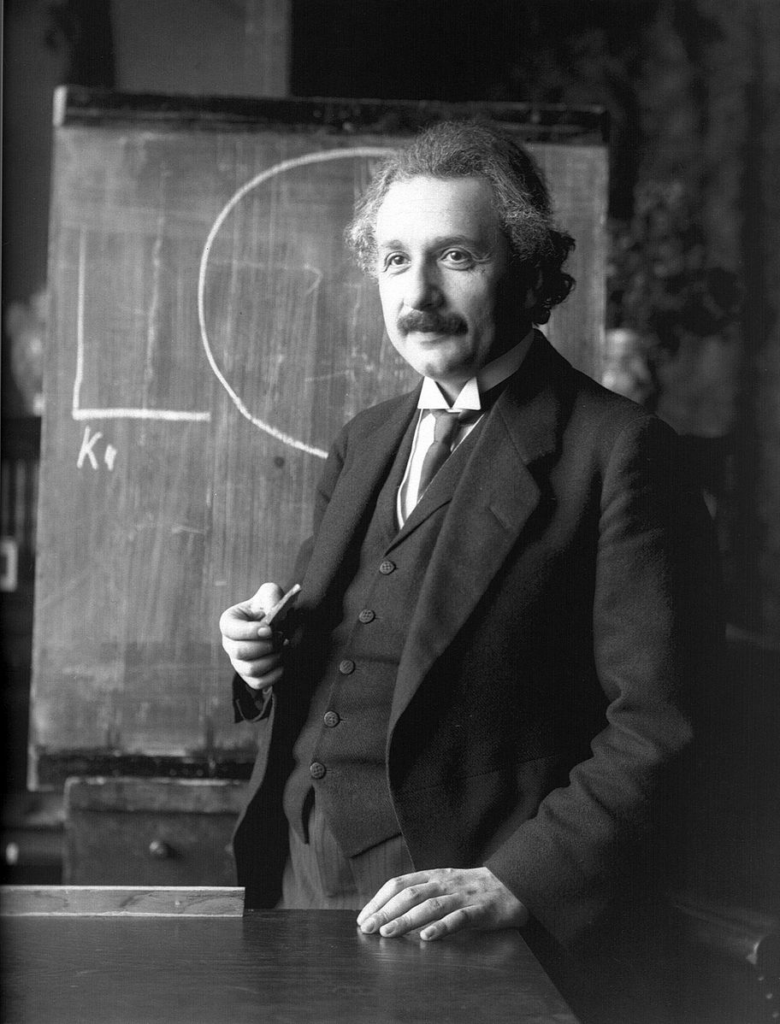by Jason Brooks
Jason Brooks, a student at the Lyndon B. Johnson School of Public Affairs, has created a website that explores the causes of World War I using the Bargaining Model of War.

(Image courtesy of “History and Theory: Explaining War”)
According to Brooks, “Employing the Bargaining Model of War will require us to understand the difference between preventive and preemptive war. It will also require us to delve methodically into the diplomatic, economic, political, and social history of the European great powers in the lead up to WWI.”

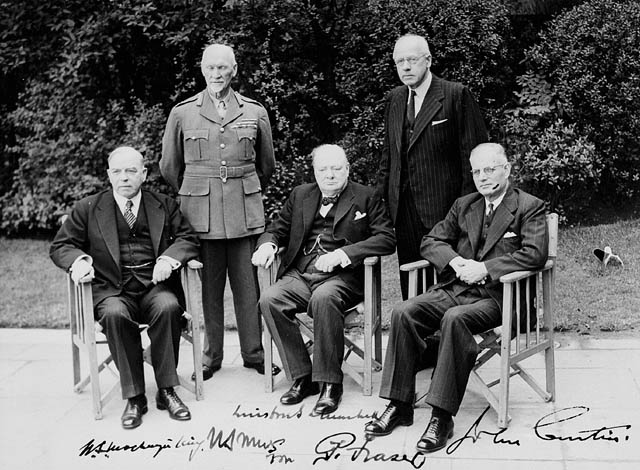
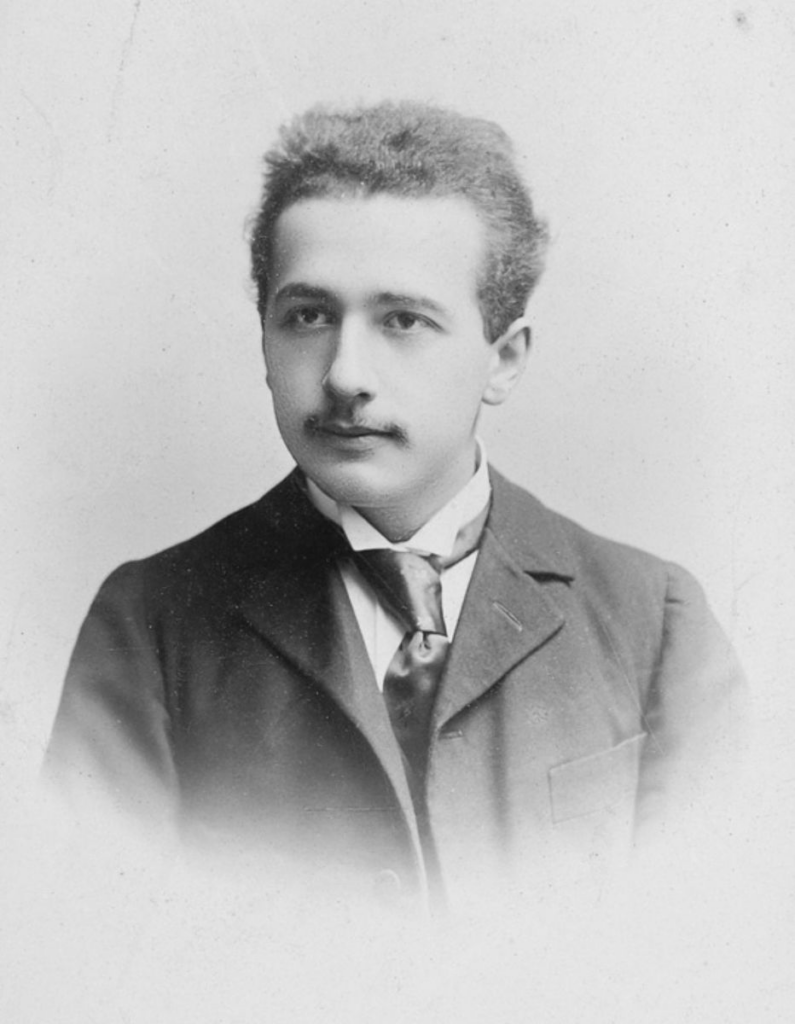
(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)
The site tells the story of World War I using international, economic, social, and political history, as well as the history of globalization, to examine how political leaders’ fear and misunderstanding of power shifts in the European continent at the turn of the twentieth century resulted in war in July of 1914. Together, Brooks’ website explores the critical intersection of international history and international relations theory, two disciplines which he believes will help students achieve a greater understanding of the cause of World War One.

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress)
University of Texas at Austin – Department of History
(Professor: Jeremi Suri)








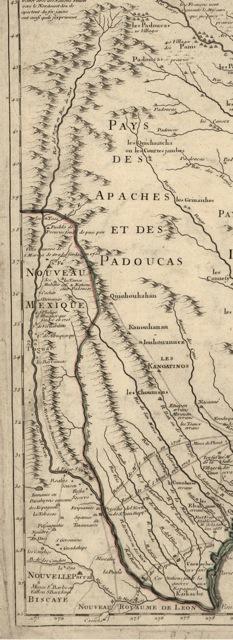





 In his sharp analysis of Britain’s declining world system,
In his sharp analysis of Britain’s declining world system,