by Amina Marzouk Chouchene | First Published by The Imperial and Global Forum
The British Empire has been firmly tied to myth, adventure, and victory. For many Britons, “the empire was the mythic landscape of romance and adventure. It was that quarter of the globe that was colored and included darkest Africa and the mysterious East.”[1] Cultural artifacts such as music, films, cigarette cards, and fiction have long constructed and reflected this rosy vision of the empire as a place of adventure and excitement. Against this widely held view of the empire, Jeffrey Auerbach identifies an overwhelming emotion that filled the psyche of many Britons as they moved to new lands: imperial boredom. Auerbach defines boredom as “an emotional state that individuals experience when they find themselves without anything particular to do and are uninterested in their surroundings.”[2]
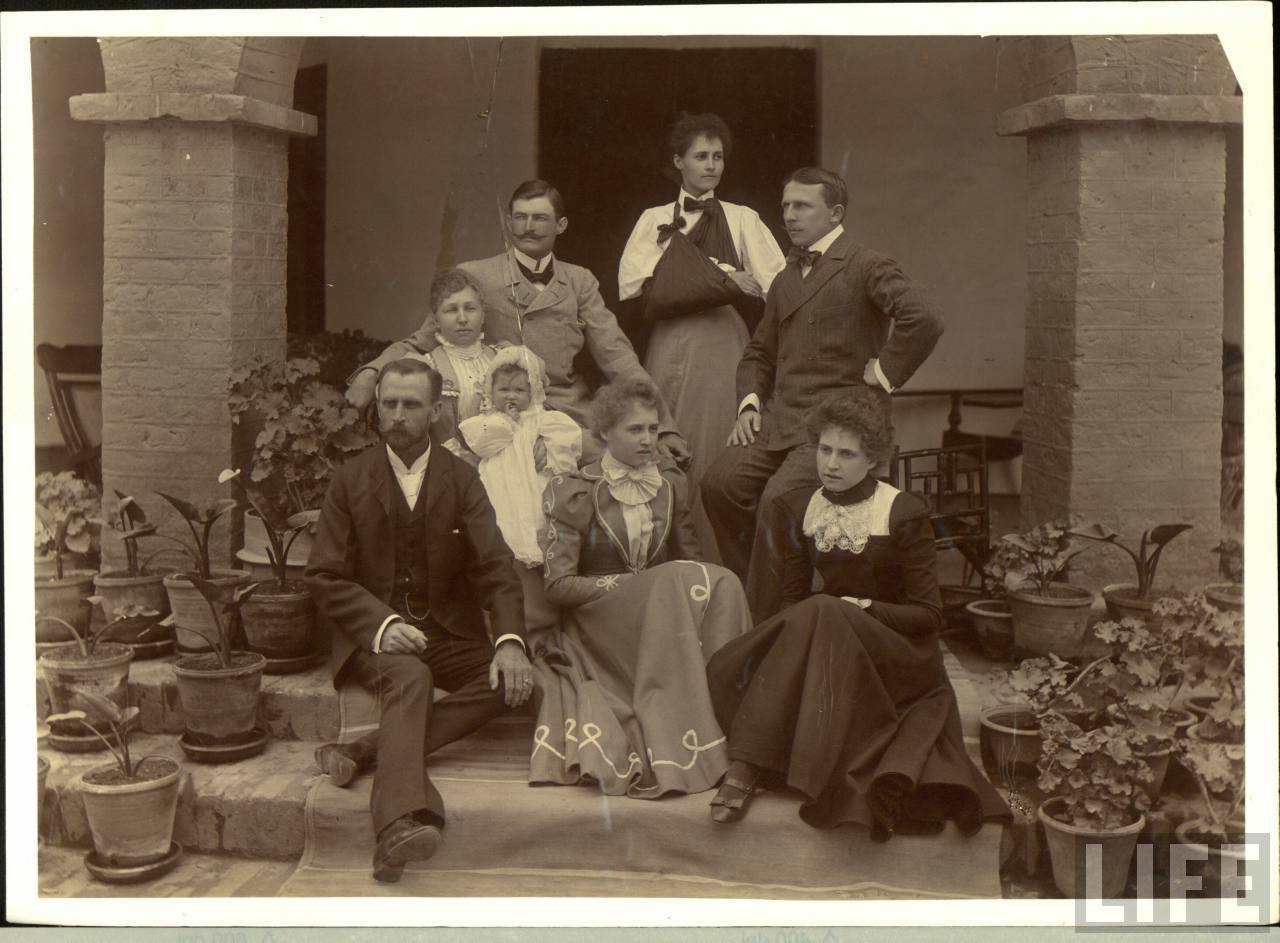

Unenthused British Men and Women in India (via Wikimedia Commons)
Auerbach identifies the feeling as a “modern construct” closely associated with the mid-eighteenth century. This does not mean that people were never bored before this, but that they “did not know it or express it.”(p.4) Rather, it was with the spread of industrial capitalism and the Enlightenment emphasis on individual rights and happiness that the concept came to the fore.
In a well-researched and enjoyable book, the author argues “that despite the many and famous tales of glory and adventure, a significant and overlooked feature of the nineteenth-century British imperial experience was boredom and disappointment.”(p.4) In other words, instead of focusing on the exploits of imperial luminaries such as Walter Raleigh, James Cook, Robert Clive, David Livingstone, Cecil Rhodes and others, Auerbach pays particular attention to the moments when many travelers, colonial officers, governors, soldiers, and settlers were gripped by an intense sense of boredom in India, Australia, and southern Africa.

Imperial Boredom by Jeffrey A. Auerbach (2018)
In five thematic chapters, “Voyages”, Landscapes,” Governors,” Soldiers”, and “Settlers,” Auerbach shines new light on the experience of traversing, viewing, governing, defending and settling the empire from the mid-eighteenth century to the early twentieth century. (p.6) The monotonous nature of the sea voyage, dreary and uninteresting imperial lands, daily routine, depressingly dull dispatches, mind-numbing meetings are some of the sources of an utter sense of imperial boredom.
Although Auerbach’s book traces imperial boredom from the mid-eighteenth to the early twentieth century, he makes it clear, from the beginning, that the sense of boredom experienced by many Britons in new colonial settings was much more profound during the nineteenth century. Indeed, the latter was marked by a series of bewildering social, cultural, and technological changes that stripped the empire of its sense of novelty. The development of new means of transport such as steamships, the rise of tourism, and the proliferation of guidebooks jeopardized the sense of risk, newness, enthusiasm that had long been associated with the British imperial experience. (p.5) Consequently, while “the early empire may have been about wonder and marvel, the nineteenth century was far less exciting and satisfying project.”(p.77)
Map of India from A Handbook for Travellers in India, Burma, and Ceylon Guidebook, 1911 (via Wikimedia Commons)
Additionally, Auerbach suggests that imperial boredom arose out of a yawning gap between the rosy vision of the empire as a thrilling experience, largely fostered by nineteenth-century fiction, and the realities on the ground. Instead of pure entertainment, colonial officers and governors were fed up with the excessively ceremonial and bureaucratic nature of the empire. They were bombarded with a burdening volume of paperwork and monotonous public duties such as hospital visits, school inspections, and state dinners.(p.8) Soldiers were engaged in mere skirmishes and spent most of their time in barracks suffering searing heat. Rarely were they able to resist the temptations of alcohol. Others deserted the army and went missing “searching for simple and transitory pleasures that might alleviate their monotony.”(p.116) Settler women incessantly complained about the dullness of their lives, interspersed with unexciting social rituals and prohibitions on contact with indigenous people.(p.9)An interesting case in point is that of British women in India, who rarely learned an Indian language or interacted with the local population due to “an imperial culture increasingly rooted in difference and aloofness.”(p.150) As a result, experiences of solitariness and a consequent sense of boredom were a ubiquitous feature of their lives. For example, Maria Graham, who visited Calcutta and Madras in 1810, complained about her inability to know any Indian family due the “distance kept up between Europeans and the natives.”(p.150) Thereupon, she was bored.
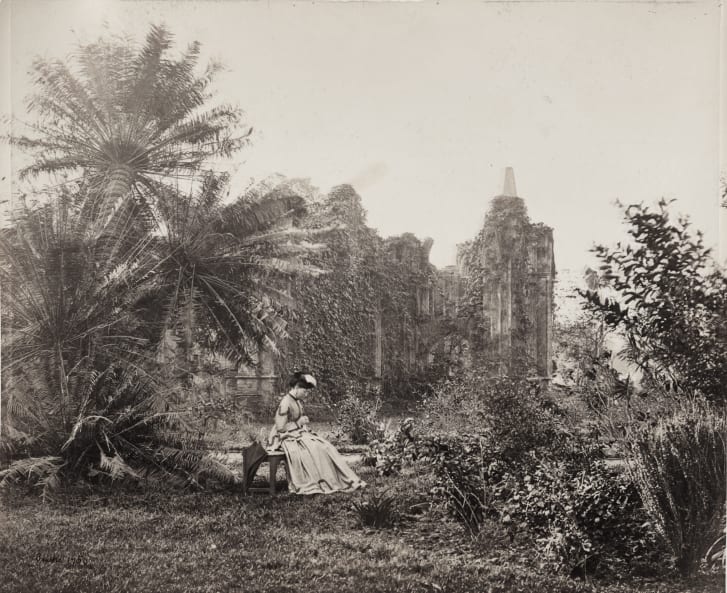

A woman sits alone in a field, 19th Century India (Photo Credit: British Library Board via CNN)
All of these examples are compellingly relevant and illustrative of some of the colonial circumstances that drove Britons mad with boredom, challenging one of the enduring myths about the British Empire as a site of exciting adventure.
![]()
[1] Jeffrey Richards, “Boy’s own Empire: Feature Films and Imperialism in the 1930s.”Imperialism and Popular Culture. edited by John Mackenzie, Manchester UP, 1986, 143.
[2] Jeffrey A. Auerbach, Imperial Boredom.
![]()
You might also like:
The November feature: History Between Memory and Reconstruction
Did the British Empire depend on separating Parents and Children?
Anxieties, Fear, and Panic in Colonial Settings: Empires on the Verge of a Nervous Breakdown edited by Harald Fischer-Tiné (2016)
The Public Archive: Mercenary Monks
Indrani Chatterjee on Monasteries and Memory in Northeast India
The Public Archive: Indian Revolt of 1857
![]()



