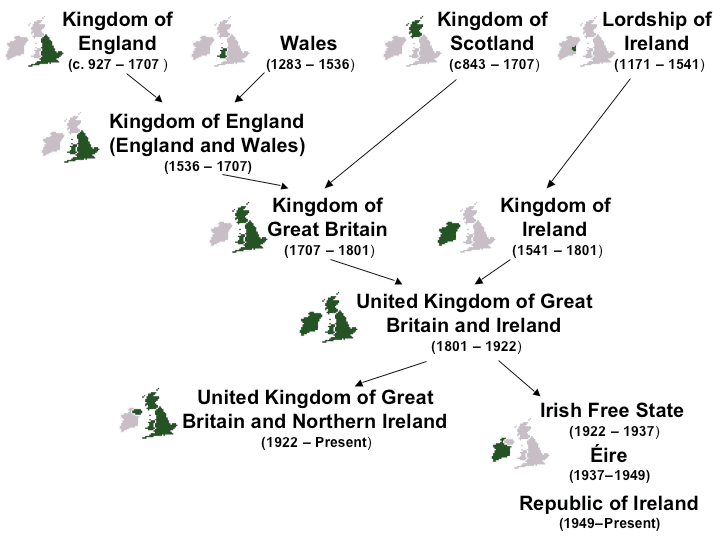
Map of England (via Wikimedia)
I came to Texas from England over thirty years ago, now. My prior experience of living in the U.S. had been during my year abroad as part of my undergraduate degree at the University of Warwick, embedded in the department of History at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Although unbeknownst to me at the time my experience in Madison proved to be pivotal and part of the chain of events that would result in my coming to UT-Austin and Texas. Two things happened as a result of my time in Madison. The first was exposure to an absolutely brilliant political scientist of Latin American history– Peter H. Smith. The second was my first trip to Mexico. After completing my year at Madison and before returning to England to complete my senior year at Warwick, I embarked on my version of Jack Kerouac’s road trip – in my case a Greyhound bus and its Mexican counterpart (solo, no less) from Madison to Mexico City. Mesmerized by my experiences in Mexico, I knew that I wanted to specialize in its history. During the writing up of my dissertation at Cambridge University, I was lucky enough to be invited for one year as a visiting professor in the History department at UT-Austin. That year was particularly memorable and as I look back I’m still not quite sure how I did what I did: prep for four new courses in a university system very different from that of Cambridge where I was used to the tutorial system; complete my dissertation that involved some commuting between Austin and Cambridge; and, oh yes, fall in love with the Texan who I would marry. In fact, in March of that memorable year, I flew to Cambridge to defend my dissertation (successfully), and flew back to Austin the next week to get married. Not bad! But, things got even better. As it turned out, the professor for whom I substituted for a year, decided not to return. I applied for the tenure-track position that opened up and was fortunate to be selected for the position. And, here I am at home in Texas and privileged to be working with creative colleagues, stimulating students, and phenomenal research resources. Plus, I never did like the English climate……
Also in this series:
Tatjana Lichtenstein
Julie Hardwick
Toyin Falola
Yoac Di-Capua