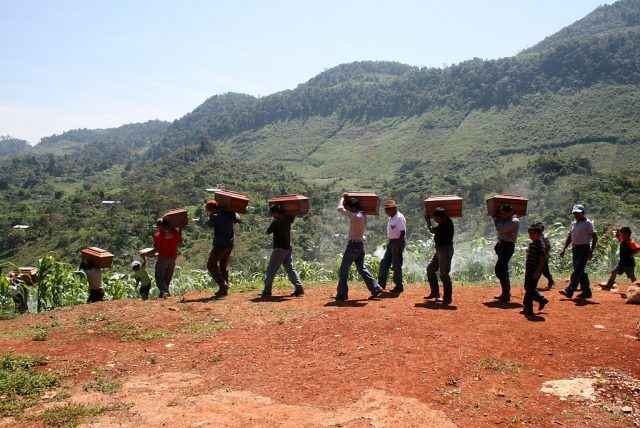
The legend of La Llorona is ubiquitous in Latin America. The tale typically centers on a woman who, upon learning of her husband’s infidelity, drowns their son and daughter in a moment of madness. She soon realizes what she has done and drowns herself in a river. Despite her contrition, she is unable to enter heaven and wails incessantly throughout the night. For this reason, she is known as La Llorona, the weeping woman.
In Jayro Bustamente’s 2019 film adaptation, La Llorona cries for her children once more. But rather than being killed by their own mother, the Guatemalan director foregrounds Enrique Monteverde (Julio Díaz), a former Guatemalan general during the nation’s civil war, as the perpetrator.
This powerful and moving film begins in Monteverde’s mansion. The elite, upper-class officer — ostensibly based on Guatemala’s infamous President Efraín Ríos Montt — is depicted in decline, struggling to breathe, and increasingly paranoid. Bustamante employs dark lighting and gaunt makeup to underscore the man’s ailing state. Yet it quickly becomes clear that Monteverde is not senile but rather haunted by the ghosts of his past. He is standing accused of genocide against the Ixil Mayas during the nation’s 36-year-long civil war.
At Monteverde’s trial, a veiled Maya woman begins testifying in a shadowy courtroom. In a beautiful-tracking shot, she recounts how the Guatemalan army arrived in her village, brutalized children, and razed her house to the ground. The grey-haired former general then takes the stand, flanked by more victims of his crimes. He declares that his intention was “to create a national identity in this country” and that he does not even understand the accusations against him. Despite his defiance, the court finds him guilty, causing Monteverde to hyperventilate before being rushed to the hospital.
![The abuelas [grandmothers] of Sepur Zarco. First row seated (from right-left): Antonia Choc (blue huipil); Felisa Cuc (orange huipil); Rosario Xo (blue huipil); Candelaria Maaz (pink huipil); Manuela Bá (light blue huipil); Demesia Yat (dark blue huipil);
Seated behind Demesia Yat (left) (wearing white huipil with green embroidery): Margarita Chub.
Standing, second row, (from right-left): Matilde Sub (pink); Catarina Caal (off-white); María Bá (purple huipil); Cecelia Xo (purple huipil); Carmen Xol (tan flowered huipil)](https://notevenpast.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/45385291432_f7d10bb473_k-1024x683.jpg)
As the defeated Monteverde and his family await the patriarch’s sentencing in their mansion, Bustamante’s La Llorona enters the picture. Alma (María Mercedes Coroy), an almost spectral Maya woman, arrives at the front door after wading through a crowd of demonstrators celebrating the guilty verdict outside. She requests work since the house’s servants have all resigned due to the former general’s increasingly erratic behavior. Distracted by Monteverde’s conviction, the family hires the woman as a housemaid despite knowing little about her.
When Alma starts her job, Bustamante unravels Monteverde’s sinister past, and the horrors of the Guatemalan Civil War, with increasing detail. The former general’s history of sexually abusing indigenous women, for example, surfaces as the otherworldly Alma compels the depraved man to watch her as she dries off in the bathroom. When the family discovers Monteverde aroused by Alma, his daughter Natalia (Sabrina De La Hoz) and granddaughter Sara (Ayla-Elea Hurtado) look at him with utter disgust. The following morning, Sara mysteriously tells her mother that Alma’s two children died. Bustamante juxtaposes these surreal scenes with slow shots of Monteverde chasing voices of wailing women down the mansion hallway with a gun. In the process, he prompts viewers to wonder if Alma has possessed the former general in retribution, or if the woman’s sheer presence has caused him to unravel from long-standing guilt.
Regardless, Monteverde and his family’s hallucinations only become more vivid the longer Alma resides in the mansion. Bustamente’s llorona eventually possesses Monteverde’s wife Carmen (Margarita Kenéfic), who previously denied her husband’s invidious history. “The past is the past,” she had claimed, “[and] if we turn around, we’ll turn into salt sculptures.” The older woman is then forced to live the murder of Alma’s children as though they were her own. Here, Bustamante’s choice to foreground Guatemalan elites’ confrontation with the war, rather than indigenous victims’ physical suffering, helps prevent watchers from being unwittingly transformed into voyeurs of violence.
Ultimately, La Llorona is an engrossing interpretation of the famous folk legend. Bustamante’s follow-up to Ixcanul (2015) and Temblores (2019) —which addressed similarly fraught topics — uncovers the civil war’s indelible imprints on Guatemalan society. His use of magical realism evinces how indigenous victims remain profoundly impacted by the army’s counterinsurgency and how perpetrators have repressed their guilt. Although Alma herself perhaps demanded more characterization, her role largely stands as a representation of the war’s victims. Her hauntings of the elite family reveal that the past is not even past in Guatemala. And only by allowing suffering to speak, or wail, will justice be realized.
The views and opinions expressed in this article or video are those of the individual author(s) or presenter(s) and do not necessarily reflect the policy or views of the editors at Not Even Past, the UT Department of History, the University of Texas at Austin, or the UT System Board of Regents. Not Even Past is an online public history magazine rather than a peer-reviewed academic journal. While we make efforts to ensure that factual information in articles was obtained from reliable sources, Not Even Past is not responsible for any errors or omissions.