By Edward Shore
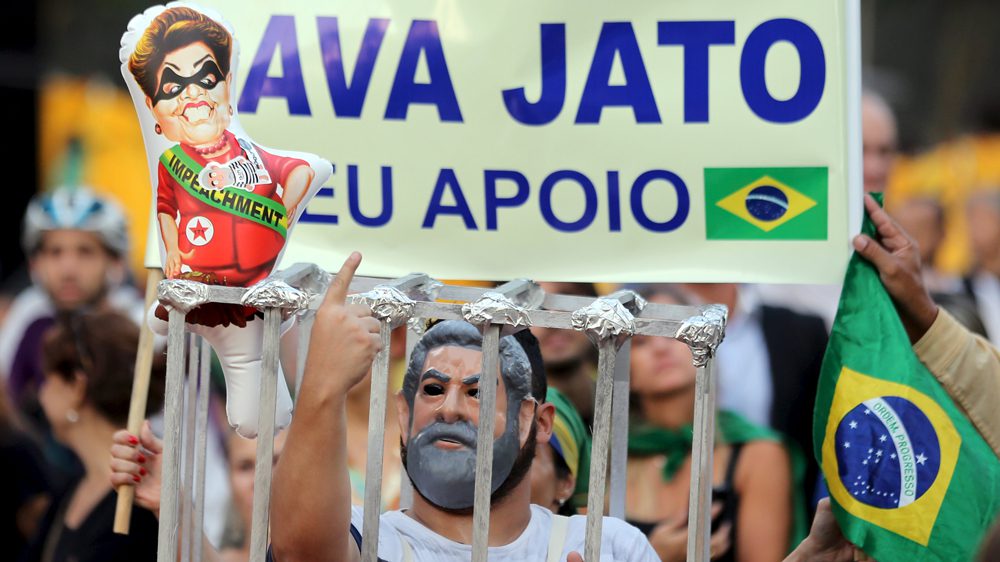
On August 31, 2016, Brazil’s senate impeached embattled President Dilma Rousseff on charges of concealing budget shortfalls with funds from a federal bank. The vote was merely a formality. The decision of the Brazilian Democratic Movement Party (PMDB) to abandon its coalition with Rousseff’s Workers’ Party (PT) had sealed the fate of Brazil’s first female president months ago. Dilma’s ouster took place amid a free falling economy and a jarring corruption scandal involving the state oil company, Petrobras, that has implicated roughly two-thirds of the Brazilian legislature and rocked the foundation of Latin America’s largest democracy. Operação Lava Jato or “Operation Car Wash” is a criminal investigation authorized by the Brazilian Federal Police that began as a money laundering probe but has since widened to investigate politicians and Petrobras executives accused of accepting bribes in return for awarding contracts to construction firms at inflated prices. Prominent members of every major party are accused of accepting bribes and stashing public funds in secret accounts in Panama and Switzerland. Brazil’s Supreme Court charged Michel Temer, Dilma’s former vice-president and current president of Brazil, with violating campaign finance laws, preventing him from seeking re-election after his term ends in 2018. His disqualification is probably moot. Temer is so unpopular that he chose not to attend the closing ceremonies of the Rio Olympic Games at Maracanã Stadium to avoid angry spectators who jeered and brandished signs calling for his resignation.
While cabinet ministers, legislators, and former presidential candidates are accused of stealing from public coffers, prosecutors have failed to bring similar charges against Rousseff. Many observers allege that her impeachment was a conspiracy to prevent further investigation into the Car Wash scandal and to remove the Workers’ Party from power after thirteen years. They suspect that Dilma’s predecessor and presumptive favorite to win the presidency in 2018, Luiz Ignácio “Lula” Da Silva, was the target of the federal investigators all along. Michel Temer and his all white male cabinet represent a stark repudiation of the PT coalition, an alliance of working people, students, intellectuals, social movement activists, women, and people of color. The administration’s proposal to slash social programs responsible for lifting millions of Brazilians out of poverty has led to violent clashes between police and demonstrators in major cities across the country September 2016. Once again, the poor and vulnerable will pay a heavy price for the sins of Brazil’s political class.
What does the fallout mean for Brazil’s traditional peoples- namely indigenous groups, rubber tappers, and rural black communities descended from fugitive slaves called quilombos? Two weeks before Dilma’s impeachment, I traveled to São Paulo’s Atlantic Rainforest to visit my friends and colleagues at the Instituto Socioambiental (ISA), an NGO that defends the social and environmental rights of traditional peoples in Brazil. I attended the Ninth Annual Quilombo Seeds Festival, a farmers’ market and seminar organized by ISA in the heartland of the Ribeira Valley, a region that is home to 88 quilombo communities and the last preserves of endangered species and wildlife in Brazil’s most heavily industrialized state. Each year, farmers and fishermen from the quilombos gather in the town of Eldorado to exchange seeds, roots, crops, livestock, fish, and oysters to promote food security and to defend against cultural loss resulting from environmental restrictions on subsistence farming and the intrusion of mineral companies on their lands.
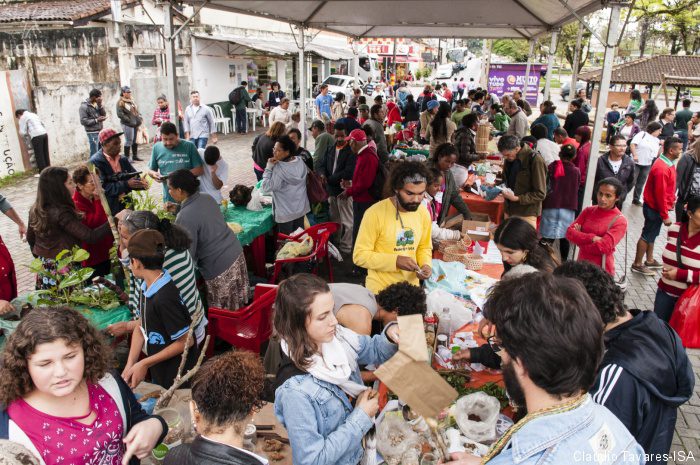

Dilma’s impending trial cast a shadow over the event. Quilombolas (individuals who identify as quilombo-descendants) feared the ouster of PT would embolden their enemies: corporate farmers, cattle ranchers, and proponents of hydroelectric dams. They also worried that Temer’s government would impose new limitations on quilombos’ constitutional rights to land. Dilma Rousseff was hardly an ardent defender of traditional peoples’ rights. Davi Pereira Júnior, a doctoral student in Latin American Studies at the University of Texas and activist from the quilombo community of Itamatatiua in Maranhão, has criticized Rousseff’s government for “closing its eyes to the assassinations of dozens of quilombo leaders who were killed in cold blood while defending their communities’ rights to land.” During Dilma’s presidency, Brazil fast tracked approval of several hydroelectric dams, including the Belo Monte project in Xingu, Pará, that will displace more than 20,000 people, including indigenous groups like the Juruna and Arara, and destroy 250 square miles of protected rainforest in the Amazon. Her administration also did little to resolve the bureaucratic impasse that has prevented thousands of quilombos from obtaining land and recognition from the government. Still, many acknowledge the situation could get worse. Much worse.
Michel Temer’s government has already curbed traditional peoples’ rights in significant ways. First, his administration axed the Ministry of Culture that previously was in charge of approving communities’ petitions for recognition as quilombo-descendant and stripped responsibility for titling quilombo lands from INCRA, the federal agency in charge of agrarian reform. Now the task of certifying quilombos and conferring land titles falls to the Ministry of Education, which lacks the funds, personnel, or expertise to carry out its responsibilities. “In this political climate, how will our communities obtain recognition? Who will take responsibility? Who is responsible for recognizing our rights?” asked Zé Rodrigues, a leader from Quilombo Ivaporunduva. Temer’s administration has eliminated the Secretary for the Promotion of Racial Equality (SEPPIR), an agency that oversaw public policies to promote education, health care, social services for quilombo communities across the country.
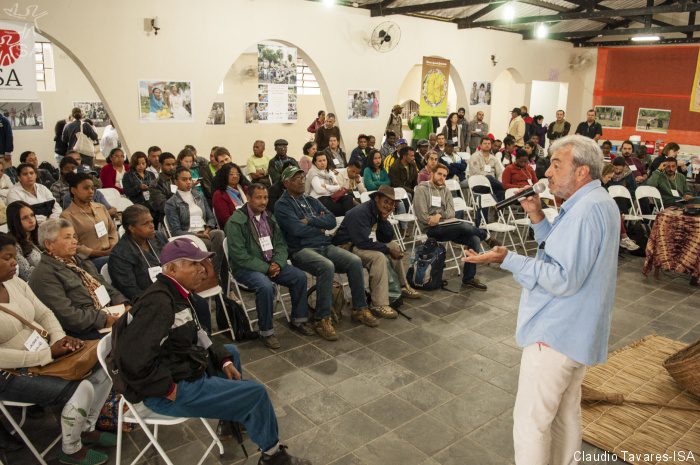

The new government also endorsed PEC 215, a proposed amendment to the constitution that seeks to delegate the Brazilian Congress, dominated by the agribusiness lobby, with the duty of recognizing and demarcating indigenous and quilombola territories. “PEC 215 represents an instrument of repression against original and traditional peoples in Brazil,” affirmed Ewerton Lobório, a human rights lawyer and staffer for Nilto Tatto, a Workers’ Party congressman from São Paulo. “The right wing has seized power by demonizing the poor and enacting legislation that takes away their guaranteed rights.” Temer’s actions have emboldened his ally, Governor Gerardo Alckmin of São Paulo, who signed a bill privatizing São Paulo’s state parks and giving mineral companies a blank check to drill for lead, zinc, and baryte in environmentally sensitive areas used by quilombos and indigenous communities for subsistence farming and fishing. In sum, Temer’s rise to power represents an assault on the hard fought rights and privileges achieved by indigenous communities, Afro-Brazilians, and traditional peoples following the return to democracy in 1985.
How can the academic community express solidarity with traditional peoples’ activists and their allies? I posed the same question on this blog last January and I’m still no closer to arriving at a definitive answer. Still, I’m convinced that the university has a role to play, at the very least, in speaking out against these violations of human rights. One way researchers can help is by organizing workshops and conferences to provide quilombola activists with a platform to publicize their struggle for rights and inclusion. Next February, LLILAS and IHS will be co-sponsoring a conference about food security and quilombos’ ongoing struggle to restore subsistence farming rights in the Atlantic Rainforest. Panelists will include representatives from the Instituto Socioambiental, experts on sustainable agriculture, and quilombola farmers fighting to restore access to subsistence garden plots called “roças.” We hope that the event will enable our guests to forge partnerships with researchers at the University of Texas who are interested in agriculture, sustainability, traditional peoples’ rights, and climate change in tropical rainforests. We also hope to apply pressure on Brazilian authorities to comply with their constitutional obligation to respect the rights of quilombo communities. “What can we do about this?” asked Davi Pereira. “Well, we can do what we’ve always done: fight to defend our rights. These rights are nonnegotiable for they guarantee the social, economic, cultural, political, and religious survival of our communities.”
Author’s note: Brazilian Federal Judge Sergio Moro brought charges against Luiz Ignácio Lula da Silva on September 20, 2016, for alleged involvement in the Car Wash Scandal.
The views and opinions expressed in this article or video are those of the individual author(s) or presenter(s) and do not necessarily reflect the policy or views of the editors at Not Even Past, the UT Department of History, the University of Texas at Austin, or the UT System Board of Regents. Not Even Past is an online public history magazine rather than a peer-reviewed academic journal. While we make efforts to ensure that factual information in articles was obtained from reliable sources, Not Even Past is not responsible for any errors or omissions.