by Priya Ramamoorthy, Kavya Ramamoorthy, Smrithi Mahadevan and Maanasa Nathan
Westwood High School
Senior Division
Group Website
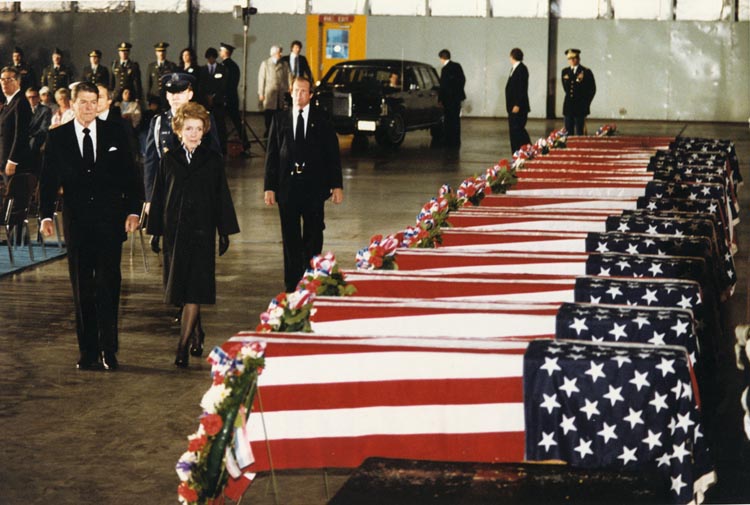
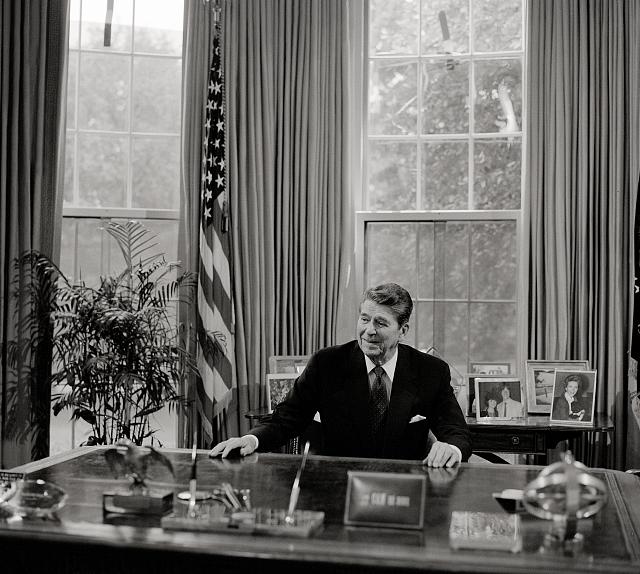
Over thirteen tense days in October, 1962, nuclear conflict nearly broke out between the United States and the Soviet Union. These global superpowers were engaged in a bitter standoff over the appearance of Soviet nuclear missiles on the newly communist island of Cuba, just 90 miles south of Florida. Fortunately, after days of diplomacy and negotiation, tensions cooled and neither side deployed their nuclear arsenal. According to Stacey Bredhoff, Curator of the Kennedy Library, those terrifying two weeks, later dubbed The Cuban Missile Crisis, “was certainly the most dangerous episode in human history.”
Westwood High School students Priya Ramamoorthy, Kavya Ramamoorthy, Smrithi Mahadevan and Maanasa Nathan won first place in the Senior Group Website category at Texas History Day with their digital report on this infamous moment in world history. The site explores the political context of the crisis, the individuals involved, key events and its aftermath. You can explore their award winning site, “The Cuban Missile Crisis” here.
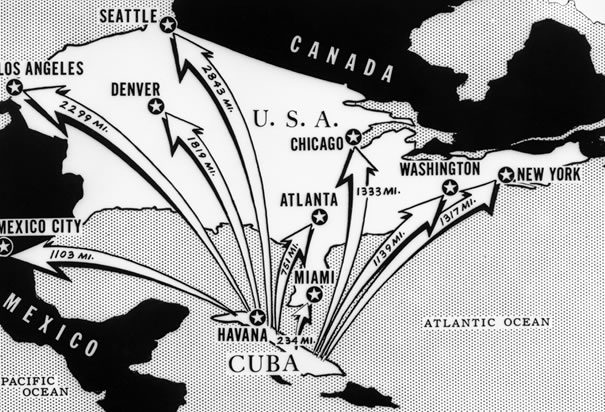
“Danger off our shores: This newspaper map shows the distances from Cuba to various cities on the North American continent.” – (Bettmann/CORBIS, TIME Magazine)
The group concludes that it was a seminal moment in not only American history but global history:
The crucible of the Cuban Missile Crisis captured the attention of President Kennedy and Premier Khrushchev and forced them to prioritize world stability over national rights. This culminated in an increased understanding of each political adversary’s perspective. The crisis proved that Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD) is an unreliable deterrent. Although fifty years have passed, its lessons remain relevant. As more nations develop nuclear weapons with each passing year, the risk of a devastating exchange increases. To prevent nuclear war diplomacy must be prioritized at all times. While exercising their sovereign rights, countries must consider the bigger picture of global stability.


















 that authoritarian governments were common in the twentieth century, lasted for several generations, and some, like the authoritarian government of North Korea, continue to affect global affairs in the new millennium. It is also increasingly evident that popular participation, and not just dictators’ decrees, helped build and dismantle authoritarian regimes.
that authoritarian governments were common in the twentieth century, lasted for several generations, and some, like the authoritarian government of North Korea, continue to affect global affairs in the new millennium. It is also increasingly evident that popular participation, and not just dictators’ decrees, helped build and dismantle authoritarian regimes.