By Peter Kunze
In a recent interview with Fusion about how Hamilton (2015) “revolutionized” Broadway for performers of color, the Tony Award-winning lead, Leslie Odom, Jr., recalled,
“I saw a reading of Hamilton at Vassar. There’s four men of color on stage, singing a song about friendship and brotherhood, and it undid me. I had never seen anything, anything like that. And I just knew that this thing was so special, and that the world needed to see it.”

Members of the Hamilton cast greet President Barack Obama in 2015, Leslie Odom, Jr. is in the center, in a blue coat (via Wikimedia commons).
There’s no denying that the decision to cast Hamilton with actors of colors—save King George—was an important decision worthy of praise. (The show has also faced criticism, though, for leaving real-life people of color out of the musical retelling.) Odom’s comment, however, should be treated with a healthy skepticism, because it unintentionally obscures the long history of musicals by, about, and for people of color. While Odom celebrates the representational politics of Hamilton, he overlooks the long history of people of color writing, producing, directing, and starring in a theater of their own, on and off Broadway. From the Chitlin’ Circuit to El Teatro Campesino, people of color have long found creative expression on stages across the United States, often when they were excluded from more mainstream venues. Diversity on Broadway remains an important issue and it’s hardly the progressive beacon one may hope. Nevertheless, several key shows and performers paved the way for Hamilton, including Lin-Manuel Miranda himself.

Lin-Manuel Miranda, Philippa Soo, Leslie Odom, Jr., and Christopher Jackson perform at the White House, March 2016 (via Wikimedia Commons).
Musical theater historians note that the Broadway musical is one of only two native-born art forms; the other is, of course, jazz. The defining moment of musical theater’s maturation for many such scholars is the 1927 premiere of Show Boat, Jerome Kern and Oscar Hammerstein II’s adaptation of Edna Ferber’s bestseller. Perhaps the most iconic moment in the show is when Joe, the African American stevedore, looks out over the Mississippi and bellows, “Ol’ Man River,” a moment immortalized on screen by Paul Robeson. Show Boat’s legacy rests upon its status as an “integrated musical”—that is, a show that seamlessly integrates the spoken dramatic portions (the “book”) with the music. Rather than musical interludes, characters break into song at moments of dramatic tension or comic relief. Sixteen years later, in 1943, Oscar Hammerstein II, now partnered with Richard Rodgers, produced Oklahoma!, which furthered the efforts to unite songs, lyrics, book, and choreography to create a serious work of dramatic literature. Critics at the time praised the arrival of a new American art form—one, of course, that was years in the making and deeply indebted to various European and American cultural traditions.
This narrative of artistic progress, promoted in large part by Oscar Hammerstein II himself, has been challenged in recent years. Last theater season, George C. Wolfe staged Shuffle Along, or, the Making of the Musical Sensation of 1921 and All That Followed, not so much a revival as a metamusical about the making of the original show (the Tony Award nominators recognized the show in the Best Musical rather than the Best Revival of a Musical category.) Wolfe argues this popular show was an important forerunner of the “integrated musical,” but equally important, it reminds us of the rich tradition of African American theater and people of color theater more broadly.
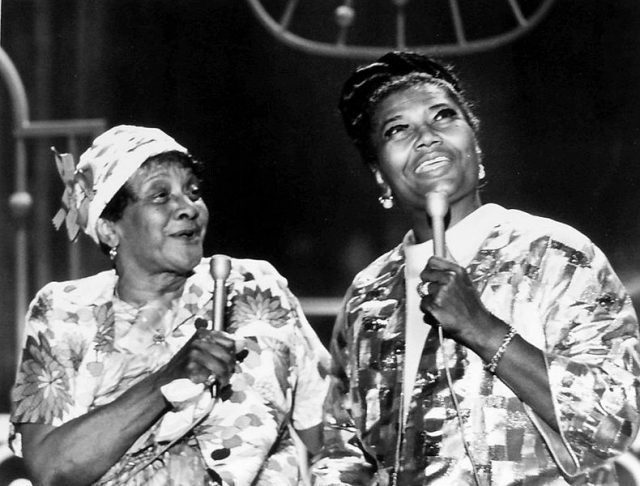

Moms Mabley and Pearl Bailey performing on The Pearl Bailey Show, February 1971 (via Wikimedia Commons).
The African American musical, in particular, has a long and storied history dating back before and including Shuffle Along. Performers like Moms Mabley, the Nicholas Brothers, and Lena Horne were featured in Broadway revues, and while Porgy and Bess (1935) was developed by white creators, the opera had an all-black cast and remains a landmark in American music. The late 1960s into the 1970s saw several all-black musicals, including Hallelujah, Baby! (1967), Raisin (1973), Your Arms Too Short to Box with God (1976), and Ain’t Misbehavin’ (1978). The most popular was The Wiz (1975), running for over 1600 performances and serving as the basis for the Diana Ross film (1978). Pearl Bailey led an all-black revival of Hello, Dolly! in 1975, furthering the practice of non-traditional casting that has sparked a good deal of debate on Broadway in recent years. In the 1980s, August Wilson began writing the “Pittsburgh Cycle,” a series of ten plays documenting black life during each decade of the 20th century. Of course, some of these shows had creative teams including or dominated by white talent, but the effort to stage black lives should not be dismissed. Many of these shows introduced or showcased the leading black talent of their respective eras.
The early 1990s saw shows like Once on This Island (1990), Five Guys Named Moe (1992), Jelly’s Last Jam (1992), and Bring in ‘Da Noise, Bring in ‘Da Funk (1996), showcasing the talents of performers like Gregory Hines, Savion Glover, and LaChanze. It also saw the debut of Audra McDonald, perhaps the pre-eminent Broadway star of her generation, having won six Tony Awards for her work in plays and musicals—more than any other stage actor ever. Shows with multiethnic casts, including Rent (1996), The Lion King (1997) and Ragtime (1998), offered a more inclusive theater and vision of America. Nevertheless, Latinx and Asian American performers on Broadway unfortunately remain less visible than their white counterparts. In recent years, the romanticized stereotypes and misguided multiculturalism found in The King and I (1951), West Side Story (1957) and Miss Saigon (1991) have been countered by a musical theater about and by people of color, including Allegiance (2015), Fela! (2009), and Miranda’s earlier effort, In the Heights (2008). Miranda also translated the lyrics of the Puerto Rican characters into Spanish for the 2009 bilingual revival of West Side Story, directed by the show’s original book writer, Arthur Laurents. Unable to compete with the spectacle and backing available to megamusicals, these shows often had relatively short runs. Hamilton, however, may be the first contemporary show to weather the storm and emerge as a long-running success on par with The Producers (2001) or The Book of Mormon (2011). In fact, Hamilton was the highest grossing show last year, followed closely by The Lion King.
At this point, it has become nearly impossible for mainstream critics and commentators to discuss Hamilton without resorting to hyperbole. It has received winning endorsements from President Obama to Oprah Winfrey as well as Tonys, a Grammy, and a Pulitzer Prize for Drama. To be sure, these accolades for creator Lin-Manuel Miranda, his production team, and the cast were well-deserved. Yet in appreciating the original contribution of Hamilton, we must not forget the shows that paved the way—shows Miranda has acknowledged in interviews and in Hamilton itself—to understand the rich, albeit complex, history of representation on the boards and behind the scenes of Broadway.
![]()
You may also like:
Charlotte Canning writes about internationalism and US theatre during the 2oth century.
NEP contributors discuss great books in US theatre history.
Julia Gossard asks, “Why is Anne Hathaway So Sad?” while examining the history behind Les Misérables.
![]()