By Mark Sheaves
 Images of American Indians are ubiquitous in contemporary US culture. Step into a convenience store and you can’t help but notice that two of the most popular tobacco brands, Redman Chewing Tobacco and Natural American Spirits, are adorned with the face of a feathered-headdress wearing chief. Approximately 2,000 high schools across the country use Native American imagery or symbolism in their name, mascots, and iconography. Sign into Netflix and you will quickly find a film with Native American characters: Disney’s Pocahontas was recently added to their library, while Adam Sandler’s The Ridiculous Six, depicting bandits and Indians in the American Wild West, was the big 2015 winter release. Shopping for fashion? The geometric patterns commonly associated with the Navajos of the Southwest have covered garments on the catwalk and in fashionable stores such as Prada and Barney’s over the past year. If you follow the NFL, you will know that Washington DC’s team wear an Indian chief on their helmets and their controversial name splashed across burgundy jerseys. And with Halloween just around the corner, people dressed in Indian costumes will party with ghosts, monsters and witches at gatherings across the country. Why is the image of the American Indian so popular in American culture? What is the history behind these images? And why does the history matter?
Images of American Indians are ubiquitous in contemporary US culture. Step into a convenience store and you can’t help but notice that two of the most popular tobacco brands, Redman Chewing Tobacco and Natural American Spirits, are adorned with the face of a feathered-headdress wearing chief. Approximately 2,000 high schools across the country use Native American imagery or symbolism in their name, mascots, and iconography. Sign into Netflix and you will quickly find a film with Native American characters: Disney’s Pocahontas was recently added to their library, while Adam Sandler’s The Ridiculous Six, depicting bandits and Indians in the American Wild West, was the big 2015 winter release. Shopping for fashion? The geometric patterns commonly associated with the Navajos of the Southwest have covered garments on the catwalk and in fashionable stores such as Prada and Barney’s over the past year. If you follow the NFL, you will know that Washington DC’s team wear an Indian chief on their helmets and their controversial name splashed across burgundy jerseys. And with Halloween just around the corner, people dressed in Indian costumes will party with ghosts, monsters and witches at gatherings across the country. Why is the image of the American Indian so popular in American culture? What is the history behind these images? And why does the history matter?

Natural American Spirit logo (via OpenCage).
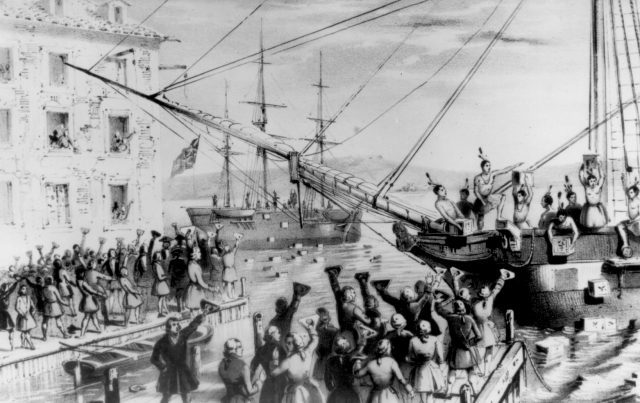
One way to answer these questions is to think about how and why white Americans have dressed or acted like Indians during the course of American history. In his classic work Playing Indian, Philip Deloria demonstrates that the act of playing Indian is as old as the USA itself. On the December 16, 1773, a group led by the Sons of Liberty boarded the Dartmouth and two other ships in Boston harbor and dumped tea into the cold water in protest over import tax. The protestors wore feathers, headdresses, and war paint and supposedly shouted Indian words in an event that would come to be known as the Boston Tea Party. The Mohawk disguises have been explained as an attempt to maintain secrecy or as a strategy to cast blame on a third party, but for Deloria they represented a political statement aimed at the English. Playing and dressing as an Indian was an act that declared a distinct American identity.
In Playing Indian, Deloria explores how and why Indians have been so important to those seeking to define what it is to be an authentic American. Largely focused on the activities and ideas of white men, Deloria argues that the practice of performing like an Indian has persisted in American culture from the eighteenth century through the 1990s when the book was published. He considers the specific meaning and significance of key events and organizations where people played Indian, including the Boston Tea Party, the New York Tammany Society, the development of anthropology as an academic discipline, the birth of the boy scouts, and during the counterculture movements of the 1960s. While the many examples Deloria offers demonstrate the importance of the Indian image in American culture for over two centuries, he argues that the “practice of playing Indian has clustered around two paradigmatic moments – the Revolution, which rested on the creation of a national identity, and modernity, which has used Indian play to encounter the authentic amidst the anxiety of urban industrial and postindustrial life.” Given the importance of these two moments in US History, Indian play has been hugely significant in the creation of American culture and identity.
Deloria organizes his thesis around two connected dimensions, an “axis of value” and an “axis of distance.” The “axis of value” highlights the positive and negative stereotypes of Indians in American culture. Deloria’s “axis of distance” captures the ways Indians have at times been included as part of American culture and at other moments been used as an external mirror to reflect what Americans should and should not be. For example, Indians have been presented as violent, pagan, drunken savages and thus the anti-thesis of a model American. This is an image that has largely served to justify appropriation of Indian lands and programs to eradicate Indian culture. Yet, ideas about Indians have also represented quintessential American values like freedom, individualism and a connection to nature and the land. In the revolutionary era, this positive idea of an Indian served those seeking to define themselves as distant from European culture. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, Native Americans were cast as exemplars of a simple life, critiquing the decadence some Americans perceived during a period of rapid industrialization and growth.
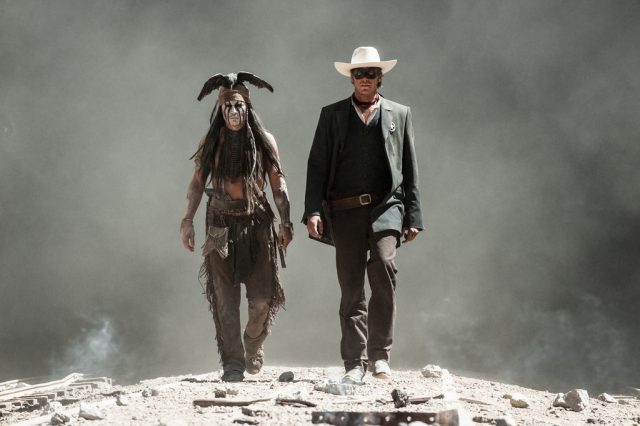

The 2013 Lone Ranger movie drew criticism for its representation of Native American culture (via Jorge Figueroa).
Deloria’s wide-ranging study demonstrates that American ideas about Indians have oscillated between positive portrayals of Indian nobility and negative associations of backwardness depending on the context and motivations of the subjects. Tensions between “desire and repulsion” and “nobility and savagery,” Deloria argues, lie at the heart of American identities, so when Americans performed as Indians, they were trying to balance the positive and negative in what they thought of as American identity. But these stereotypes of Native Americans that developed from the practice of playing Indian continue to inform dealings with Native people, that keep them in subordinate social, political, legal, and economic positions. The act of playing Indian, then, matters to contemporary Native Americans.
So as Halloween rolls around, the long and complicated history of playing Indian that Deloria describes should make us all think about reaching for the faux turquoise bead jewelry, braiding our hair, or picking up a plastic bow and arrow. The costumes we wear carry political messages from a history that people may not know, but that continues to shape the experiences of Native Americans living today.
Philip J. Deloria, Playing Indian (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1999)
![]()
Read more by Mark Sheaves on Not Even Past:
Francisco de Miranda: A Transatlantic Life in the Age of Revolution 1750-1816, by Karen Racine (2002)
The Web of Empire, By Alison Games (2008)
Philip of Spain, King of England, by Harry Kelsey (2012)
You may also like:
Nakia Parker reviews Black Slaves, Indian Masters: Slavery, Emancipation, and Citizenship in the Native American South, by Barbara Krauthamer (2013).
![]()